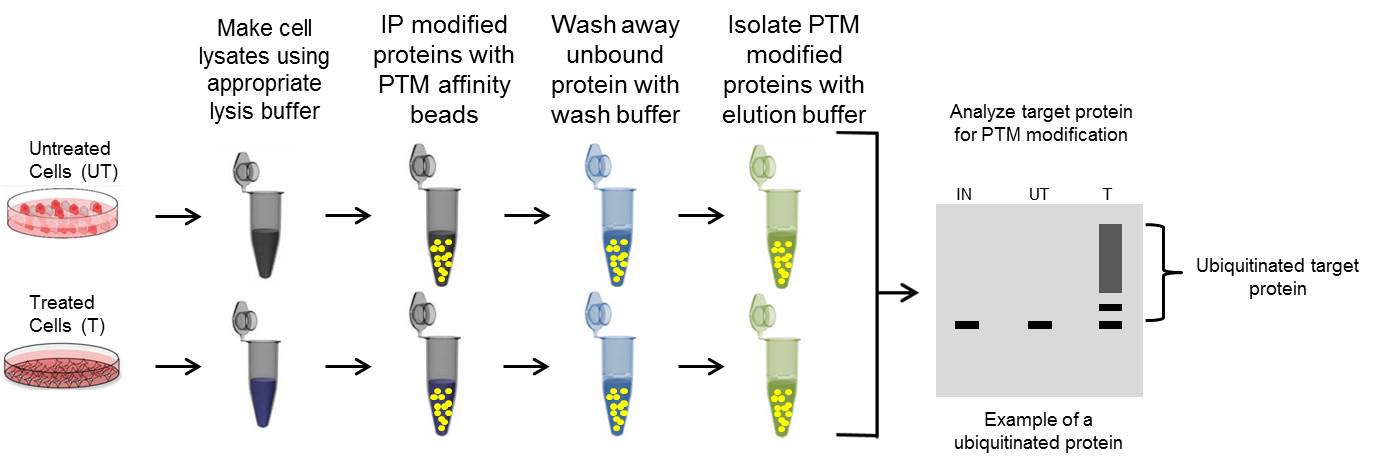
PTM Immunoprecipitation Protocol
A. Lysis Buffer
Many standard immunoprecipitation IP protocols recommend isolating in a gentle lysis buffer if possible to minimize protein denaturation, while still isolating your target protein. However, with PTM IP choosing the optimal lysis buffer is based on three criteria: 1) Isolating target protein of interest, 2) utilizing a buffer that is compatible with affinity reagents, and 3) minimize protein: protein interactions to decrease the possibility of false positive identifications [1].
Thus, it is recommended to lyse in a denaturing buffer to isolate proteins from all cellular compartments while disrupting the majority of protein interactions. Prior to IP the lysate should be diluted with an appropriate dilution buffer to maintain the integrity of the affinity reagents.
Denaturing lysis buffers have two drawbacks. 1) They produce viscous lysates due to genomic DNA, and 2) They may not be compatible with conventional colorimetric protein assays.
Denaturing lysis buffer options:
BlastR lysis system (BLR01) for optimized PTM IP and detection.
Note: contains filters to remove genomic DNA contamination and is compatible with standard colorimetric assays for accurate protein measurements. Click here for a detailed analysis using the BlastR Rapid Lysate Prep kit.
1% SDS denaturing lysis buffer
8M Urea
6M Guanidinium-HCl
B. Preparing Cell Lysates with Denaturing Lysis Buffer
It is recommended to aim for 0.5-1.0 mg of total protein lysate per IP assay as an optimal starting point.
Protein yield varies widely for any given cell line, and it is strongly recommended to perform a “test plate” protein quantitation, particularly if you are unsure of the expected protein yield from your experimental conditions using a denaturing lysis buffer.
1. Prepare lysis and dilution buffers by adding the appropriate protease and de-PTM inhibitors (e.g. deubiquitinase inhibitor, phosphatase inhibitors)
2. Remove media and rinse cells twice with ice-cold 1X PBS
3. Ensure that as much PBS as possible has been removed to ensure maximal efficacy of lysis buffer
4. Lyse cells with 1X denaturing lysis buffer
5. Scrape cells off the plates.
Note: The lysate should become viscous and this is a good indicator of efficient lysis.
6. Remove gDNA contamination.
Option A: Pass the lysate through BlastR filter (BLR02), Time:10 seconds.
Option B: Sonicate samples, Time: optimize based on machine.
Option C: Pass the lysed suspension 5–10 times through a needle attached to a 1 mL syringe, Time: about 5-15 minutes.
Note: Ensure the viscosity is completely reduced. DNA contamination can interfere with protein quantitation and IP steps.
7. Optional: Heat samples to 95°C for 5 min. This step is dependent on the denaturing lysis buffer used.
8. Microcentrifuge for 10 minutes at 14,000 X g, 4°C, and transfer the supernatant to a new tube.
9. Dilute the suspension with 1X dilution buffer. Mix gently.
10. Quantitate Protein concentration. At this point lysate can be stored at –80°C.
Note: This step is important when comparing lysates from different conditions.
Proceed with the immunoprecipitation
Click here for a detailed protocol for cell culture or tissue lysate prep using the BlastR Rapid Lysate Prep kit.
C. Immunoprecipitation with Antibody Conjugated to Beads
Optional: It may be necessary to perform a lysate pre-clearing step to reduce non-specific binding to the affinity beads (See section below).
Note: All IPs should be performed with appropriate controls for accurate data interpretation
1. Add 1mg of cell lysate to the recommended amount of affinity bead complex. Incubate on a rotating platform for 1-2hr 4°C.
2. Pellet beads by spinning for 30 seconds at 3-5000 X g at 4°C in a microcentrifuge.
3. Remove supernatant without disturbing bead pellet.
4. Wash pellet with of 1X wash buffer. Wash step is often performed with dilution buffer. Do not use denaturing lysis buffer for wash steps.
5. Pellet beads by spinning for 30 seconds at 3-5000 X g at 4°C in a microcentrifuge.
6. Remove supernatant without disturbing bead pellet.
7. Repeat the wash step (4-6) two more times.
8. Add elution buffer and resuspend the beads by gently tapping/flicking the side of the tube.
9. Place the spin column in a fresh collection tube and centrifuge at 9-10,000 x g for 1 minute at room temperature to collect the IP sample.
10. Place samples in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. Collect sample by centrifugation at 10,000 X g for 1 minute at RT.
Proceed with the western blot analysis
Click here for an optimized protocol using Signal-Seeker PTM detection kits
D. Immunoprecipitation with Unconjugated Antibody
1. Add 1mg of lysate to the recommended dilution of primary antibody. Incubate on a rotating platform for 1h-overnight at 4°C.
Note: Incubation time is dependent on the primary antibody
2. After incubation with primary antibody, add either protein A or G agarose beads (20-40 μl of 50% bead slurry). Incubate on a rotating platform for 1–4 hours at 4°C.
3. Remove supernatant without disturbing bead pellet.
4. Wash pellet with of 1X wash buffer. Wash step is often performed with dilution buffer. Do not use denaturing lysis buffer for wash steps.
5. Pellet beads by spinning for 30 seconds at 3-5000 X g at 4°C in a microcentrifuge.
6. Remove supernatant without disturbing bead pellet.
7. Repeat the wash step (4-6) two more times.
8. Add elution buffer and resuspend the beads by gently tapping/flicking the side of the tube.
9. Place the spin column in a fresh collection tube and centrifuge at 9-10,000 x g for 1 minute at room temperature to collect the IP sample.
10. Place samples in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. Collect sample by centrifugation at 10,000 X g for 1 minute at RT.
Note: Utilizing an unconjugated antibody for IP will result in high levels of heavy and light chain contamination. If examining proteins at 50 and 25kDa alternative methods are recommended
Cell Lysate Pre-Clearing (Optional)
1. Add 1mg of cell lysate and to control beads. (For conjugated beads, isotype conjugated beads are the best option)
2. Incubate at 4°C for 60 minutes.
3. Spin for 2 minutes, 5000 X g, at 4°C. Transfer the supernatant to a fresh microcentrifuge tube.
4. Proceed to step 1 of Immunoprecipitation.
Reference:
Emmerich CH, Cohen P. Optimising methods for the preservation, capture and identification of ubiquitin chains and ubiquitylated proteins by immunoblotting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(1):1-14.
Additional Links:



