Myosin II protein: rabbit skeletal muscle
Product Uses Include
- Measurement of F-actin activated myosin ATPase activity
- Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect myosin II ATPase activity
- Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect the myosin II - F-actin interaction
- Control myosin ATPase activity in drug discovery screening projects
Material
Myosin II protein has been purified from rabbit skeletal muscle. The full length myosin II protein has been purified with its essential light chains (ELC) and regulatory light chains (RLC), see Figure 1 and 2. Myosin II has been determined to be biologically active in an F-actin activated ATPase assay. Rabbit skeletal muscle myosin II is not recommended for use in motility assays. Rabbit myosin II protein is supplied as a white lyophilized powder. When reconstituted in nanopure water, the protein will be in the following buffer: 25 mM PIPES-NaOH pH 7.0, 1.25 M KCl, 2.5% sucrose and 0.5% dextran. The lyophilized protein is stable at 4°C desiccated (<10% humidity) for 1 year.
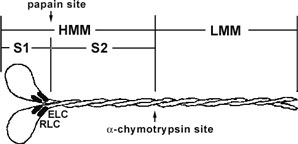
Figure 1. Diagrammatic representation of the myosin II protein and its subfragments. Myosin II or conventional myosin is a hexameric protein consisting of two heavy chains and two light chains. Myosin II can be proteolytically cleaved into heavy meromyosin (HMM, Cat.# MH01) and light meromyosin (LMM) by α-chymotrypsin. Heavy meromyosin consists of the myosin head subfragment-1 domain (S1), its associated light chains (essential light chains and regulatory light chains), and the coiled-coil subfragment -2 domain. Light meromyosin consists of coiledcoil protein structure. The myosin S1-subfragment is produced by papain digestion of HMM.
Purity
Protein purity is determined by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on a 4-20% gradient polyacrylamide gel. Myosin protein is 95% pure (see Figure 2).
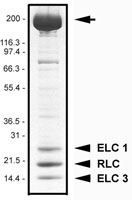
Figure 2. Myosin II protein purity determination. A 20 µg sample of MY02 was separated by electrophoresis in a 4-20% SDS-PAGE system, and stained with Coomassie Blue. Arrow indicates the myosin heavy chain (approx. 200 kDa), arrowheads indicate the RLC (approx. 20 kDa) and two ELC isoforms (approx. 25 and 17 kDa). Protein quantitation was performed using the Precision Red Protein Assay Reagent (Cat.# ADV02).
Biological Activity
The biological activity of rabbit myosin II is determined from its rate of F-actin activated ATP hydrolysis. A standard biological assay for monitoring ATP hydrolysis by myosin consists of an in vitro F-actin ATPase assay (Cat. # BK054). Stringent quality control ensures that in the presence of F-actin, rabbit myosin will have a minimum hydrolysis rate 10 fold greater than in the absence of F-actin, which is comparable to published results.
For product Datasheets and MSDSs please click on the PDF links below. For additional information, click on the FAQs tab above or contact our Technical Support department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com
Question 1: Does this myosin contain both light and heavy chains and all other subunits?
Answer 1: Yes, this protein is full length myosin motor protein isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. The myosin protein contains the two heavy chains and two light chains, the essential light chain (ELC) and regulatory light chain (RLC).
Question 2: Does this myosin have ATPase activity that is activated by actin filaments?
Answer 2: Yes, the biological activity test for the myosin protein is in vitro measurement of myosin’s ATPase activity in the activating presence of actin filaments. Stringent quality control ensures that in the presence of F-actin, rabbit skeletal muscle myosin will have a minimum hydrolysis rate 10 fold greater than in the absence of F-actin.
If you have any questions concerning this product, please contact our Technical Service department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com








