Total RhoA ELISA Application Notes
Cytoskeleton now offers the first and only commercially availble RhoA ELISA. It is recommended to use the BK150 kit in conjunction with the RhoA G-LISA™ kit (BK124), allowing quantitation of Total RhoA and Active RhoA in the same lysates.
RhoA Pathway Mechanisms
RhoA signal transduction pathways are now well recognized as major therapeutic targets for diseases such as cancer, erectile dysfunction, diabetes, hypertension and Alzheimer’s. The protein is thought to be functional only when in the active “GTP-bound” state which, in most transduction processes, comprises 0.5-5% of total RhoA. Normalization of active RhoA against total RhoA is required for accurate comparison of RhoA activity between samples. The table below highlights the mechanistic insights that can be gained by measuring these parameters.
Boulter, E., Garcia-Mata, R., Guilluy, C., Dubash, A., Rossi, G., Brennwald, P. and Burridge, K. Regulation of Rho GTPase crosstalk, degradation and activity by Rho GDI1. Nature Cell Biol. 12: 477-484 (2010).
Jin, L., Lui, T., Lagoda, G., Champion, H., Bivalacqua, T. and Burnett, A. Elevated RhoA/Rho-kinase activity in the aged rat penis: mechanism for age-associated erectile dysfunction. FASEB J. 20:536-538 (2006).
Thomas, S., Overdevest, J., et al., Src and Caveolin-1 Reciprocally Regulate Metastasis via a Common Downstream Signaling Pathway in Bladder Cancer. Cancer Res. 71:832-841 (2011).
Karlsson, R., Pedersen, E.D., Wang, Z., and Brakebusch, C. Rho GTPase Function in Tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1796:91-98 (2009).
Normalization of RhoA activation levels in transfection assays
Normalization of Active RhoA against Total RhoA is required for accurate comparison of RhoA activity between samples. Normalization of active RhoA signal is particularly important in studies that involve prolonged exposure of cells to conditions that might influence RhoA pathways, e.g. transfections or prolonged drug studies.
Cytoskeleton Inc. has developed an ELISA that allows rapid and quantitative determination of Total RhoA (Cat # BK150). The G-LISA and ELISA kit have been developed so that cell lysates are compatible with both assays. It is therefore extremely straightforward to utilize the RhoA ELISA with RhoA G-LISA samples.
The normalized fold activation of RhoA in any given cell lysate can be determined using the simple formula given below (see Fig. 1):
G-LISA value (ng) x 100 = normalized % Active RhoA
ELISA value (ng)
Example: RhoA activation by treatment with calpeptin
Method
Swiss 3T3 cells were grown to 50% confluency in DMEM media plus 10% FCS. They were then serum starved for 48h. Half of the cells were treated with 0.1 mg/ml calpeptin (Cat# CN01) for 30 minutes to activate RhoA. The other half were not treated. All cells were subsequently lysed in G-LISA lysis buffer (Part# GL36) and frozen as 12.5 µg aliquots ready for analysis by G-LISA (Fig. 2) and ELISA (Fig. 3) assays.
Results
The RhoA G-LISA data in Fig.2 show 12.5 µg lysate contained 0.37 ng of Active RhoA in calpeptin-treated cells and 0.1 ng of Active RhoA in serum-starved cells.
The Rho ELISA data in Fig.3 show 12.5 µg lysate contained 12 ng Total RhoA in calpeptin-treated cells and 11 ng Total RhoA in serum-starved cells.
Data Analysis
The fold activation of calpeptin-treated cells can be determined using the simple formula given below:
G-LISA value (ng) x100 = normalized % Active RhoA in a given lysate
ELISA value (ng)For calpeptin-treated lysates
0.37 x 100 = 3.1% Active RhoA in stimulated cells
12For serum-starved lysates
0.10 x 100 = 0.91% Active RhoA in untreated cells
11
Thus, the normalized fold activation for calpeptin-treated cells compared to untreated serum-starved cells is 3.4 fold.
In the present example Total RhoA is very similar in the two conditions (control and treated) because cells have only been briefly treated with an activator. Cell culture experiments involving repeating treatments or manipulations (drugs or transfection) are likely to have significant variation in total RhoA levels between control and experimental samples.
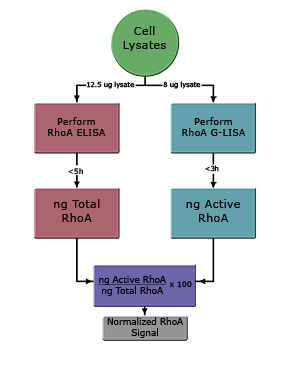
Figure 2: Determination of Active RhoA by G-LISA
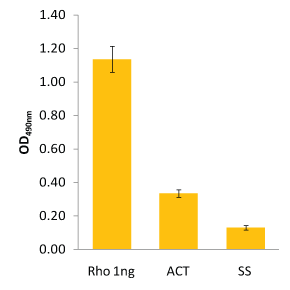
The colorimetric RhoA G-LISA (BK124) was carried out as detailed in the protocol. Recombinant His-Rho protein (1 ng) was included as a quantitation control. Signal from 12.5 µg of calpeptin-activated lysate (ACT) and 12.5 µg of serum-starved lysate (SS) were determined to have 0.37 ng and 0.1 ng of active RhoA, respectively. Note: OD values are background subtracted.
Figure 3: Determination of Total RhoA by ELISA
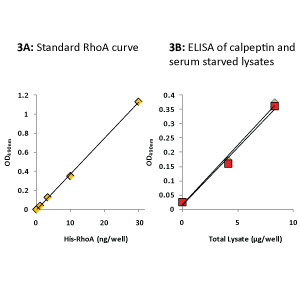
The colorimetric RhoA ELISA (BK150) was carried out as detailed in the protocol. Recombinant His-Rho protein (1-30 ng) was used to generate a standard curve for Total RhoA quantitation.
Data for 8 µg of total lysate was used to extrapolate that 12.5 µg of calpeptin-activated lysate (yellow triangles) and 12.5 µg of serum-starved lysate (red squares) contained 12 ng and 11 ng of Total RhoA, respectively.
Performance and Specifications
Sensitivity and Linearity
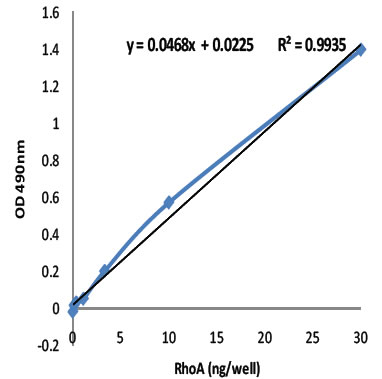
Figure 1: The Total RhoA ELISA was evaluated for sensitivity and linearity using purified recombinant human RhoA (Cat# RH01) in a range from 30 ng/well to 0.25 ng/well. The R2 value of 0.9935 indicates that the assay is highly linear from 1 ng to 30 ng/well RhoA. Cytoskeleton's 1x G-LISA Lysis Buffer is recommended for extract.
Specifications
| Linear range (ng/well or lane) | 1 to 30 ng |
| Sensitivity (i.e. +/-ng/well or lane) | 0.5 ng |
| Detection limit (ng/well or lane) | 0.1 ng |
| Coefficient of variation at OD 0.50 two replicates | 3.5% |
| Coefficient of variation at OD 0.50 eight replicates | 2.6% |
| Coefficient of variation at OD 0.50 forty-eight replicates | 2.3% |
| Z'-factor* | 0.73 |
| * Z'-factor is calculated as Zhang et al. J Biomol Screen. 1999:4(2):67-73 | |
Advantages of the RhoA ELISA
As with all ELISA assays, the advantages over Western blot analysis include speed, sensitivity, consistency, superior quantitations, simple standardizations and high throughput capacity. The availability of an ELISA formatted to measure total RhoA also provides a user friendly companion product to the RhoA activation G-LISA™ assays. Thus normalizing RhoA activation to total RhoA can now be performed utilizing all the advantages offered by a complete ELISA solution.
Assay Principle
The Total RhoA ELISA kit is designed as a highly selective sandwich ELISA format for total RhoA measurement. Each well is pre-coated with an anti-Rho IgY antibody which has high affinity for all Rho isotypes. The complementary antibody is a mouse monoclonal highly selective for RhoA. Bound RhoA is subsequently detected with a secondary antibody-HRP conjugate and the OPD substrate.
The assay is particularly flexible in its ability to detect RhoA in a wide variety of species, including human, mouse, rat, guniea pig, xenopus, drosophila, zebra fish and porcine samples.
Kit Contents - Enough reagents for 96 assays.
- 96 well Total Rho binding plate
(12 strips of 8 wells each) - Anti-RhoA antibody
- Secondary Antibody - HRP
- Rho control protein
- Dilution Buffer
- Wash Buffer (PBST)
- Antigen Presenting Buffer
- HRP Detection Reagents
