Citation Spotlight: RhoA and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in in vivo and in vitro models of sepsis-induced intestinal dysfunction
- By Cytoskeleton Inc. - Small G-Protein News
- Feb 6, 2020

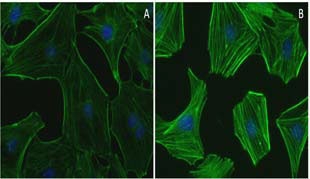
Sepsis and the accompanying systemic inflammatory response are an over-reaction of an organism’s immune system in response to infection or injury which results in organ dysfunction/failure if untreated. A healthy intestinal barrier is a primary defense against these pathogenic processes. Here, the authors investigate how NLRP3 inflammasome and RhoA participate in sepsis-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and their functional status after treatment with astragaloside IV (AS-IV), a bioactive compound from Astragalus membranaceus. In in vivo (cecal ligation and puncture mice) and in vitro (Caco-2 cells treated with lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) models of sepsis, AS-IV alleviated barrier dysfunction (e.g., decreased mouse mortality, cytokine release, and barrier permeability and increased tight junction expression in vivo; reduced cytokine levels, improved gut barrier function absent cytotoxicity in vitro). NLRP3 inflammasome and RhoA activities were elevated in intestinal tissues and Caco-2 cells and correspondingly reduced after AS-IV administration. Furthermore, a cell-permeable Rho activator prevented the effects of AS-IV, while a cell-permeable Rho inhibitor antagonized LPS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cytoskeleton’s RhoA G-LISA activation assay kit, cell-permeable Rho activator, and Rho inhibitor (Cat. # BK124, CN03, CT04, respectively) were essential in identifying RhoA (and NLRP3 inflammasome) as the molecular targets of AS-IV in the alleviation of sepsis-induced barrier dysfunction.
Products used in this citation: