Kinesin heavy chain motor domain protein (KIF5A): GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant
Product uses
- Measurement of microtubule-activated ATPase activity
- Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect motor ATPase activity
- Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect kinesin motility
- Identification/characterization of proteins or small molecules that affect motor/microtubule interactions
Material
The conserved motor domain of human Kinesin Heavy Chain (KIF5A) has been produced in a bacterial expression system. The recombinant protein contains a GST-tag at the amino terminus and has a combined calculated molecular weight of approximately 70 kDa. The protein has been determined to be biologically active in a microtubule-activated ATPase assay. The protein is supplied as a white lyophilized powder.
Purity
Protein purity is determined by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on an SDS gradient gel. Figure 1 shows 10 µg of KR01 protein that was determined to be 88% pure. The major contaminant at approximately 30 kDa is GST protein. The microtubule-activated ATPase activity of the Kinesin Heavy Chain is not inhibited by this contaminant.
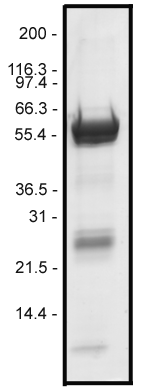
Figure 1. Kinesin Heavy Chain Motor Protein Purity Determination. A 10 µg sample of recombinant Kinesin Heavy Chain Motor Domain protein was separated on a 420% SDS gel along with Mark12 molecular weight markers (Invitrogen) and stained with Coomassie Blue. The fusion protein has an approximate molecular weight of 65 kDa. Protein quantitation was determined using the Precision Red™ Protein Assay reagent. (Cat. # ADV02)
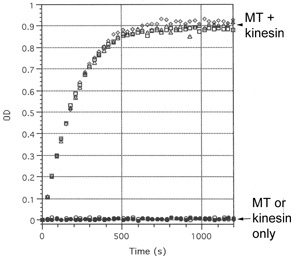
Biological Activity - Microtubule Activated ATPase Assay
Kinesin Heavy Chain ATPase activity was measured by monitoring real time free phosphate generation using the Kinesin ELIPA Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK060). The assay is based upon an absorbance shift (330 nm—360 nm) that occurs when 2-amino-6mercapto-7-methylpurine ribonucleoside (MESG) is catalytically converted to 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine in the presence of inorganic phosphate (Pi). One molecule of Pi will yield one molecule of 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine in an essentially irreversible reaction. Hence, the absorbance at 360 nm is directly proportional to the amount of Pi generated in the kinesin ATPase reaction.
For product Datasheets and MSDSs please click on the PDF links below. For additional information, click on the FAQs tab above or contact our Technical Support department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com
Coming soon! If you have any questions concerning this product, please contact our Technical Service department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com