Therapeutic targeting of the Ubiquitin Pathway
FDA Approved Ubiquitin PTM Pathway Drugs
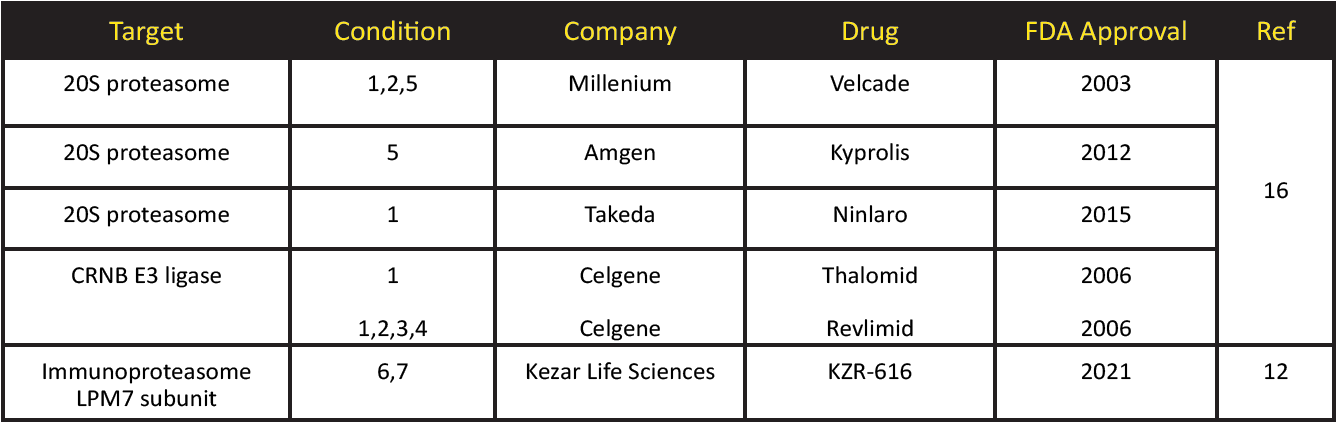
Condition Key: (1) multiple myeloma (2) mantle cell lymphoma (3) follicular lymphoma (4) myelodysplastic syndrome (5) refractory multiple myeloma (6) polymyositis (7) dermatomyositis
References
1.Khoury GA et al. 2011. Proteome-wide post-translational modification statistics: frequency analysis and curation of the swiss-prot database. Sci. Rep. 1:90
2.Krassowski M et al. 2018. ActiveDriver DB: human disease mutations and genome variation in post-translational modification sites of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D901-D910
3.Ferguson F. & Gray N. 2018. Kinase inhibitors: the road ahead. Nat. Rev.17:353-376
4.Ganesan A et al. 2019. The timeline of epigenetic drug discovery: from reality to dreams. Clin. Epigen. 11:174
5.Qin W et al. 2019. Research progress on PARP14 as a drug target. Front. Pharmacol. 10:172
6.Chen Z & Sun LJ. 2009. Nonproteolytic function of ubiquitin in the cell. Mol. Cell 33:275-286
7.Schenkein D. 2002. Proteasome inhibitors in the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Clin. Lymphoma 1:49-55
8.Kimura H et al. 2015. New insights into the function of the immunoproteasome in immune and nonimmune cells. J. Imm. Res. 2015:ID 541984
9.Althof N. et al. 2018. The immunoproteasome-specific inhibitor ONX 0914 reverses susceptibility to acute viral myocarditis. EMBO Mol. Med. Doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708089
10.Zhang C et al. 2020. Immunoproteasome-selective inhibitors: the future of autoimmune diseases? Future Med. Chem. 12:269-272
11.Kezarlifesciences.com/pipeline
12.Biospace.com/article/release/kezar-life-sciences-announces-orphan-drug-designations-for-kzr-616-for-the-treatment-of-polymyositis-and-dermatomyositis/
13. Mansour MA. 2018. Ubiquitination: friend or foe in cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 101:80-93
14. Lui et al. 2021. E3 ubiquitin ligase in anticancer drug resistance: recent advances and future potential. Frontiers Pharmacol. 12:645864
15.Lopez-Girona A, et al.2012. Cereblon is a direct protein target for immunomodulatory and antiproliferative activities of lenalidomide and pomalidomide. Leukemia 26:2326-2335
16.Weathington NM & Mallampalli RK. 2014. Emerging therapies targeting the ubiquitin proteasome system in cancer. J. Clin. Inv. 124:6-12
17.Khoury K et al. 2012. P53 Mdm2 inhibitors. Curr. Pharm Des. 18:4668-4678
18.Fang Y et al. 2020. Small-molecule MDM2/X inhibitors and PROTAC degraders for cancer therapy: advances and perspectives. Acta Pharma. Sinica B 10:1253-1278
19.Zhou X et al. 2021. Pharmacological activation of p53 triggers viral mimicry response thereby abolishing tumor immune evasion and promoting anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Disc. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290
20.Gutierrez-Diaz BT et al. 2020. Deubiquitinases: Pro-oncogenic activity and therapeutic targeting in blood malignancies. Trends Immunol. 41:327-340
21.Nawrat A. 2020. Exploring the promise of DUBs: Mission teams up with Pfizer. www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/features/mission-pfizer-dubs/
22.Zhang W & Sidhu S. 2018. Allosteric inhibitors hit USP7 hard. Nat. Chem. Bio. 14:110-111
23.Gavoy G et al. 2018. Discovery and characterization of highly potent and selective allosteric USP7 inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14: 118-125
24.Zou Y et al. 2019. The PROTAC technology in drug development. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:21-30
Signal Seeker™ PTM Detection Kits
New Signal-Seeker™ Acetyl-Lysine Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK163)
New Signal-Seeker™ Acetyl-Lysine Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK163-S)
Signal-Seeker™ Phosphotyrosine Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK160)
Signal-Seeker™ Phosphotyrosine Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK160-S)
Signal-Seeker™ Ubiquitination Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK161)
Signal-Seeker™ Ubiquitination Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK161-S)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 2/3 Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK162)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 2/3 Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK162-S)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 1 Detection Kit (30 Assay) (Cat. # BK165)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 1 Detection Kit (10 Assay) (Cat. # BK165-S)