Mitochondrial Acetylation: Emerging Concepts and Therapeutic Potential
General Overview of Lysine Acetylation in Health and Disease
Acetylation of the epsilon amino group of lysine residues (Nε-acetylation) is an ancient, highly conserved post-translational modification (PTM)1,2 that links acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) metabolism and cellular signaling. This occurs largely through the opposing activities of lysine acetyl transferases (KATs) and lysine deacetylases (KDACs)3. In humans, there are 3 major KAT families (GCN5, CBP/p300, and MYST) that all use acetyl-CoA as an essential cofactor to donate an acetyl group to target lysine residues. There are two KDAC families, the zinc-dependent histone deacetylases (HDAC1-11) and the NAD+-dependent sirtuins (SIRT1-7)1-3.
It is well documented that acetylation of nuclear histones plays a major role in regulating chromatin compaction and transcriptional activity wherein acetylation favors a more open, transcriptionally active chromatin1. Recent proteomic studies have identified over 4,500 non-histone proteins as targets of acetylation, thereby establishing lysine acetylation as a major global PTM. This PTM is present in many, if not all, cellular compartments, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and mitochondria4. Functionally, reversible lysine acetylation has been shown to regulate enzyme activity4-6, protein-protein interactions7, and protein localization and stability8,9. In addition, it plays critical regulatory roles in many cellular processes, including gene expression, cellular metabolism, apoptosis, cytoskeleton regulation, and membrane trafficking10.
In 2006, Vorinostat became the first FDA approved drug targeting histone epigenetics through HDAC inhibition for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTLC)11. There are now four FDA approved HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of CTLC, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma12, which clearly demonstrates the potential of targeting lysine acetylation for therapeutic intervention. Clinical success, coupled to the vast expansion in identification of non-histone acetyl lysine targeted proteins, has enhanced interest in exploring the regulatory functions and therapeutic potential of this PTM beyond epigenetics. The remainder of this Newsletter focuses on lysine acetylation in the mitochondria and its possible value as a therapeutic target.
Mitochondrial Lysine Acetylation
Lysine acetylation is abundant in mitochondria, with an estimated 700 proteins (63%) undergoing this modification, three fold higher than phospho-modifications in this organelle13. Elucidating the mechanisms that regulate mitochondrial acetylation and identifying potential therapeutic targets is a new and rapidly growing area of investigation10. In recent years, some general concepts have begun to emerge which are briefly outlined below:
- Lysine acetylation is highly prevalent in enzymes of the major mitochondrial metabolic pathways and many of these proteins are hyper-acetylated4.
- There is some sequence selectivity for mitochondrial protein acetylation as shown in a preference for negatively charged residues in the immediate vicinity of the acetylation site and a strong preference for hydrophobic residues at position +24.
- Mitochondrial protein acetylation changes rapidly in response to cellular nutrient availability or energy status and is likely a major mechanism regulating energy homeostasis14. It also appears that the levels of mitochondrial KATs and KDACs are tightly controlled by nutrient availability15. The link between pathological disruption of energy homeostasis and mitochondrial acetylation holds great therapeutic potential14.
- Lysine acetylation has broadly been correlated with inhibition of mitochondrial enzyme activity, particularly in oxidative metabolism13. It is, however, noteworthy that of the 700 or so acetylated mitochondrial proteins, less than 40 have been characterized at the mechanistic level13, and there are cases where acetylation may either activate or inhibit the same protein depending on the tissue type6,15.
- Several groups have proposed a non-enzymatic mechanism for mitochondrial lysine acetylation, and the relative contribution of enzymatic vs non-enzymatic regulation remains to be determined16-18.
- Low stoichiometry (< 1-5%) that translates to critical and regulated biological responses is a norm for PTMs and is one of the reasons that it is technically challenging to study these modifications19,20. Low stoichiometry often reflects the highly dynamic nature and subcellular localization of the modified proteins and their role in cell signaling19,20. Stoichiometry of acetylation in mitochondrial proteins appears to follow this trend23,24. Understanding how sub-stoichiometric levels of PTMs can have significant effects on mitochondrial function remains an open question13,23,24.
- PTM crosstalk is recognized as a major cell regulatory mechanism25. Mitochondrial actetylation has been shown to participate in PTM crosstalk as exemplified by the regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex via the hierarchical coordination of kinase, phosphatase, acetyltransferase, and deacetylase activities21.
- Heart disease and heart failure are strongly correlated with increased acetylation of mitochondrial proteins in this organ22, and multiple reports have shown that the major mitochondrial deacetylase, Sirtuin 3 (Table 1), exerts a protective function against heart disease26,27. Currently, there is intense interest in targeting SIRT3 and the mitochondrial acetylome for therapeutic intervention28,29.
- As shown in Table 1, the presence of mitochondrial KATs has only recently been described; however, they are considered to have strong therapeutic potential as targets for a variety of human diseases including cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and obesity (see references in Table 1).
Table 1: Mammalian Mitochondrial Acetyltransferases and Deacetylases
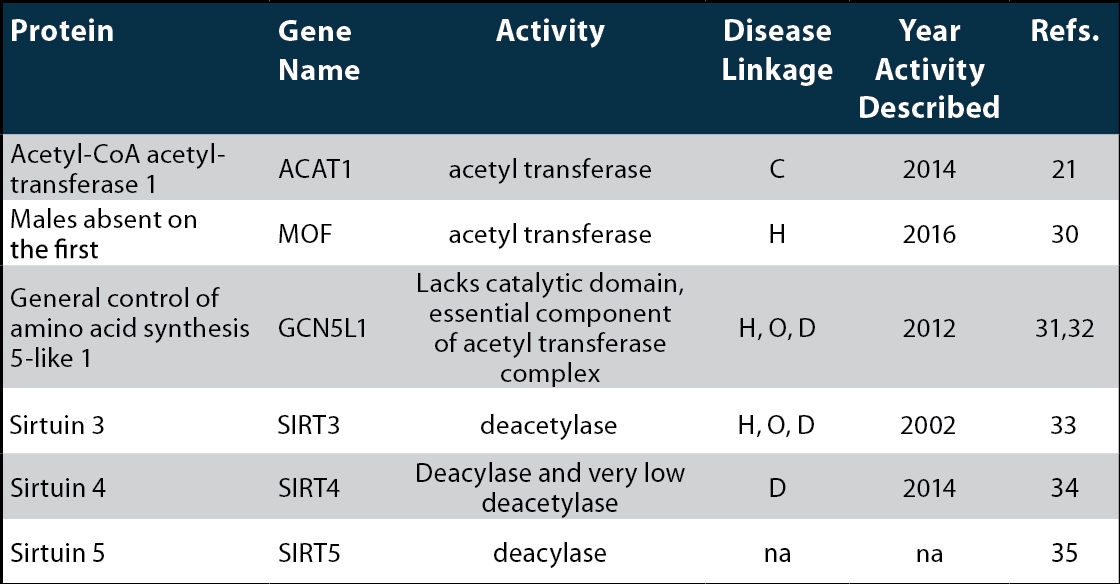
C-cancer, H-heart disease, O-obesity, D-diabetes
Conclusion
Therapeutic exploitation of the mammalian mitochondrial acetylome offers great potential for the treatment of human disease; however, it is clear that much is still to be learned about the basic biology of this PTM beyond epigenetics. The role of lysine acetylation in the cytoplasm, plasma membrane, and other cellular compartments is also an area of high interest. In this regard, the development of an expanded toolset to aid in this research is urgently needed.
Related Products & Resources
Signal Seeker™ Kits
New Signal-Seeker™ Acetyl-Lysine Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK163)
New Signal-Seeker™ Acetyl-Lysine Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK163-S)
Signal-Seeker™ Phosphotyrosine Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK160)
Signal-Seeker™ Phosphotyrosine Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK160-S)
Signal-Seeker™ Ubiquitination Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK161)
Signal-Seeker™ Ubiquitination Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK161-S)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 2/3 Detection Kit (30 assay) (Cat. # BK162)
Signal-Seeker™ SUMOylation 2/3 Detection Kit (10 assay) (Cat. # BK162-S)
PTM Antibodies, Beads, Etc
New Acetyl-Lysine Antibody Mouse Monoclonal (7B5A1) (Cat. # AAC02)
New Acetyl-Lysine-HRP Antibody Mouse Monoclonal (19C4B2.1) (Cat. # AAC03-HRP)
Phosphotyrosine Affinity Beads (Cat. # APY03-beads)
SUMOylation 2/3 Affinity Beads (Cat. # ASM24-beads)
Ubiquitination Affinity Beads (Cat. # UBA01-beads)
References
- Kim G.W. and Yang X.J. 2011. Comprehensive lysine acetylomes emerging from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 211-220.
- Weinert B.T. et al. 2011. Proteome wide mapping of the Drosophila acetylome demonstrates a high degree of conservation of lysine acetylation. Sci. Signal. 4, ra48
- Choudhary C. et al. 2014. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Bio. 15, 536-550.
- Lundby A. et al. 2012. Proteomic analysis of lysine acetylation sites in rat tissues reveals organ specificity and subcellular patterns. Cell Rep. 2, 419-431.
- Samant S.A. et al. 2014. SIRT3 deacetylates and activates OPA1 to regulate mitochondrial dynamics during stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 34, 807-819.
- Bharathi S.S. et al. 2013. Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) protein regulates long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by deacetylating conserved lysines near the active site. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 33837-33847.
- Wei L. et al. 2013. Oroxylin A induces dissociation of hexokinase II from the mitochondria and inhibits glycolysis by SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of cyclophilin D in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 4, e601.
- Inuzuka H. et al. 2012. Acetylation-dependent regulation of Skp2 function. Cell. 105, 179-193
- De Boor S. et al. 2015. Small GTP-binding protein Ran is regulated by post translational lysine acetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 112, E3679-E3688.
- Drazic A. et al. 2016. The world of protein acetylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1864, 1372-1401.
- Mann B.S. et al. 2007. FDA approval summary: vorinostat for treatment of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncologist. 12, 1247-1252.
- Yoon S. and Eom G.H. 2016. HDAC and HDAC inhibitor: from cancer to cardiovascular diseases. Chonnam Med. J. 52, 1-11.
- Baeza J. et al. 2016. Mechanisms and dynamics of protein acetylation in mitochondria. Trends Bio. Sci. 41, 231-244.
- Anderson K.A. and Hirschey M.D. 2012. Mitochondrial protein acetylation regulates metabolism. Essays Biochem. 52, 23-35.
- Thapa D. et al. 2017. Acetylation of mitochondrial proteins by GCN5L1 promotes ehnhanced fatty acid oxidation in the heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 313, H265-H274.
- Wagner G.R. and Payne R.M. 2013. Widespread and enzyme-independent Ne-acetylation and Ne-succinylation of proteins in the chemical conditions of the mitochondrial matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 29036-29045.
- Davies M.N. et al. 2016. The acetyl group buffering action of carnitine acetyltransferase offsets macronutrient-induced lysine acetylation of mitochondrial proteins. Cell Rep. 14, 243-254.
- Hosp F. et al. 2017. Lysine acetylation in mitochondria: from inventory to function. Mitochondrion. 33, 58-71.
- Johnson H. and Eyers C.E. 2010. Analysis of post-translational modifications by LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol. Biol. 658, 93-108.
- Thompson J. et al. 2012. https://genome.duke.edu/sites/default/files/ABRF_Poster_JWT_2012_PTMs.pdf.
- Fan J. et al. 2014. Tyr phosphorylation of PDP1 toggles recruitment between ACAT1 and SIRT3 to regulate the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Mol. Cell. 53, 534-548.
- Stram A.R. et al. 2017. Progressive mitochondrial protein lysine acetylation and heart failure in a model of Friedreich’s ataxia cardiomyopathy. Plos One. 12, e0178345.
- Weinert B.T. et al. 2014. Acetylation dynamics and stoichiometry in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Systems Biol. 10, 716.
- Weinert B.T. et al. 2015. Analysis of acetylation stoichiometry suggests that SIRT3 repairs nonenzymatic acetylation lesions. EMBO J. 34, 2620-2632.
- Venne S.A. et al. 2014. The next level of complexity: crosstalk of posttranslational modifications. Proteomics. 14, 513-524.
- Chen T.S. et al. 2015. Mouse SIRT3 attenuates hypertrophy-related lipid accumulation in the heart through the deacetylation of LCAD. Plos One. 10, e0118909.
- Koentges C. et al. 2015. SIRT3 deficiency impairs mitochondrial and contractile function in the heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 110, 36.
- Lee C.F. et al. 2015. Mitochondrion as a target for heart failure therapy. Circ. J. 79, 1863-1870.
- Pillai V.B. Et al. 2010. Exogenous NAD blocks cardiac hypertrophic response via activation of SIRT3-LKB1-AMP-activated kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 3133-3144.
- Chatterjee A. et al. 2016. MOF acetyl transferase regulates transcription and respiration in mitochondria. Cell. 167, 722-738.
- Scott I. et al. 2012. Identification of a molecular component of the mitochondrial acetyltransferase programme: a novel role for GCN5L1. Biochem. J. 443, 655-661.
- Wang L. et al. 2017. GCN5L1 modulates cross-talk between mitochondria and cell signaling to regulate Fox01 stability and gluconeogenesis. Nat. Comm. 8, 523-534.
- Schwer B. et al. 2002. The human silent information regulator (Sir)2 homologue hSIRT3 is a mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent deacetylase. J. Cell Biol. 158, 647-657.
- Mathias R.A. et al. 2014. Sirtuin 4 is a lipoamidase regulating pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity. Cell. 159, 1615-1625.
- Tan M. et al.2014. Lysine glutarylation is a protein posttranslational modification regulated by SIRT5. Cell Metab. 19, 605-617.

