PAK-PBD beads (binds active Rac/Cdc42 proteins)
Product Uses Include
- Measurement of the GTP/GDP ratio of Rac or Cdc42 in vitro.
- Quantitation of GTP-Rac/Cdc42 from tissue and tissue culture cell lysates.
Material
The Rac/Cdc42 (p21) binding domain (PBD) of the human p21 activated kinase 1 protein (PAK) protein has been expressed as a GST-fusion protein in E. coli. This protein binds binds specifically to GTP-bound, and not GDP-bound, Rac and Cdc42 proteins. The domain can therefore be used to specifically precipitate active, GTP-bound Rac and Cdc42 as well as to specifically block the activity of Rac and Cdc42 in vitro and in vivo.
The GST-PAK-PBD contains residues 67-150 of PAK. This region includes the highly conserved CRIB motif plus sequences required for the high affinity interaction with GTP-Rac and GTP-Cdc42.
The protein is supplied in a glutathione agarose bound format and is shipped lyophilized. The beads are colored for ease of use. This product is used in our Cdc42 and Rac activation assay Biochem Kits™ (Cat. # BK034 and BK035, repectively). The GST-PAK-PBD is also available as a free protein (Cat. # PAK01).
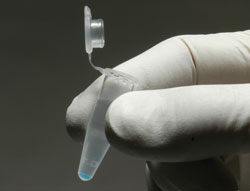
Figure 1. The brightly colored glutatione agarose beads in PAK02 are easy to use.
Purity
Protein purity is determined by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on a 12% SDS polyacrylamide gel. GST-PAK-PBD protein is >80% pure (see Figure 2).

Figure 2: GST-PAK-PBD protein purity determination. A 10 µg sample of PAK02 was separated by electrophoresis in a 12% SDS-PAGE system and stained with Coomassie Blue. The GST-PAK-PBD protein runs at approximately 34 kDa.
Biological Activity
PAK-PBD protein specifically recognizes and binds the active, GTP-bound, forms of the Rac and Cdc42 proteins. It has a much lower affinity for the inactive, GDP-bound, forms of Rac and Cdc42. When coupled to a colored glutathione sepharose matrix, the PAK-PBD protein beads become a convienent tool for assaying the activity of the Rac and Cdc42 proteins. The quality control biological assay for PAK-PBD protein beads consists of a Rac protein pulldown from human platelet extracts loaded with either GTPγS (Cat. # BS01) or GDP.
For product Datasheets and MSDSs please click on the PDF links below. For additional information, click on the FAQs tab above or contact our Technical Support department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com
Question 1: How much of the beads should I use for my pull-down experiments?
Answer 1: PAK-PBD-GST beads (Cat. # PAK02) will bind to Cdc42 or Rac1-GDP with a much lower affinity than Cdc42 or Rac1-GTP. If too many PAK-PBD beads are added to the pull-down assay, there will be significant binding to inactive (GDP-bound) Cdc42 or Rac1. The result of this will be an underestimation of Cdc42 or Rac1 activation. For this reason, we highly recommend performing a bead titration to determine optimal conditions for any given Cdc42 or Rac1 activation or inactivation assay. Once optimal conditions have been established, bead titrations should no longer be necessary. We recommend 10, 15 and 20 μg bead titrations.
Question 2: How can I test whether the beads are working properly?
Answer 2: A standard biological assay for PAK-PBD GST protein beads consists of a Rac or Cdc42 protein pull-down from cells loaded with either GTPγS (Cat. # BS01) or GDP. Here are guidelines to follow (see PAK02 datasheet for more details):
Positive Cellular Protein Control:
Total cell lysate (300 – 800 μg) should be loaded with GTPγS as a positive control for the pull-down assay. The following reaction details how to load endogenous Rac1 or Cdc42 with the nonhydrolysable GTP analog (GTPγS). This is an excellent substrate for PAK-PBD beads and should result in a strong positive signal in a pull-down assay.
a) Perform GTP loading on 300 – 800 μg of cell lysate (0.5 mg/ml protein concentration) by adding 1/10th volume of Loading Buffer.
b) Immediately add 1/100th volume of GTPγS (200 μM final concentration). Under these conditions 5 - 10% of the Rac1 or Cdc42 protein will load with non-hydrolysable GTPγS and will be “pulled down” with the PAK-PBD beads in the assay.
c) Incubate the control sample at 30°C for 15 min with gentle rotation.
d) Stop the reaction by transferring the tube to 4°C and adding 1/10th volume of STOP Buffer.
e) Use this sample immediately in a pull-down assay.
Negative Cellular Protein Control:
This reaction should be performed in an identical manner to the Positive Control reaction except that 1/100th volume of GDP (1 mM final concentration) should be added to the reaction in place of the GTPγS. Loading endogenous Rac1 or Cdc42 with GDP will inactivate Rac1 or Cdc42 and this complex will bind very poorly to PAK-PBD beads.
If you have any questions concerning this product, please contact our Technical Service department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com.