
KIF5B is the founding member of the kinesin superfamily, described in 1985. It is a motor protein belonging to the kinesin-1 family that transports various cargoes along microtubules, playing a critical role in intracellular trafficking and organelle positioning. It is essential for neuronal function, vesicle transport, and maintaining cellular organization, with defects linked to several diseases and cellular dysfunctions.
The wild-type human motor domain of KIF5B is produced in a bacterial expression system.
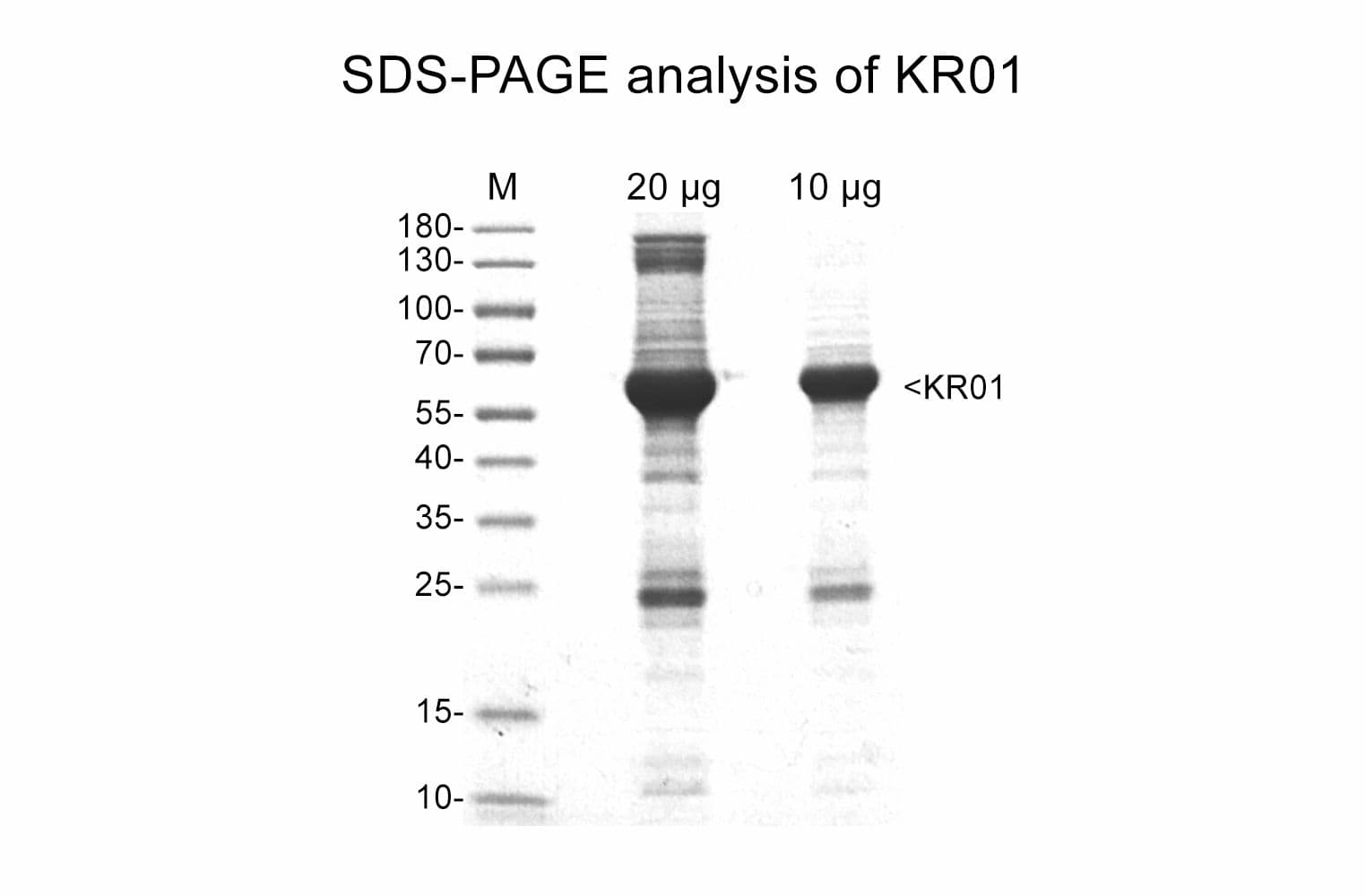
Protein purity is assessed by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue-stained protein on a4-20% polyacrylamide gel. Purity is determined to be >85% pure.
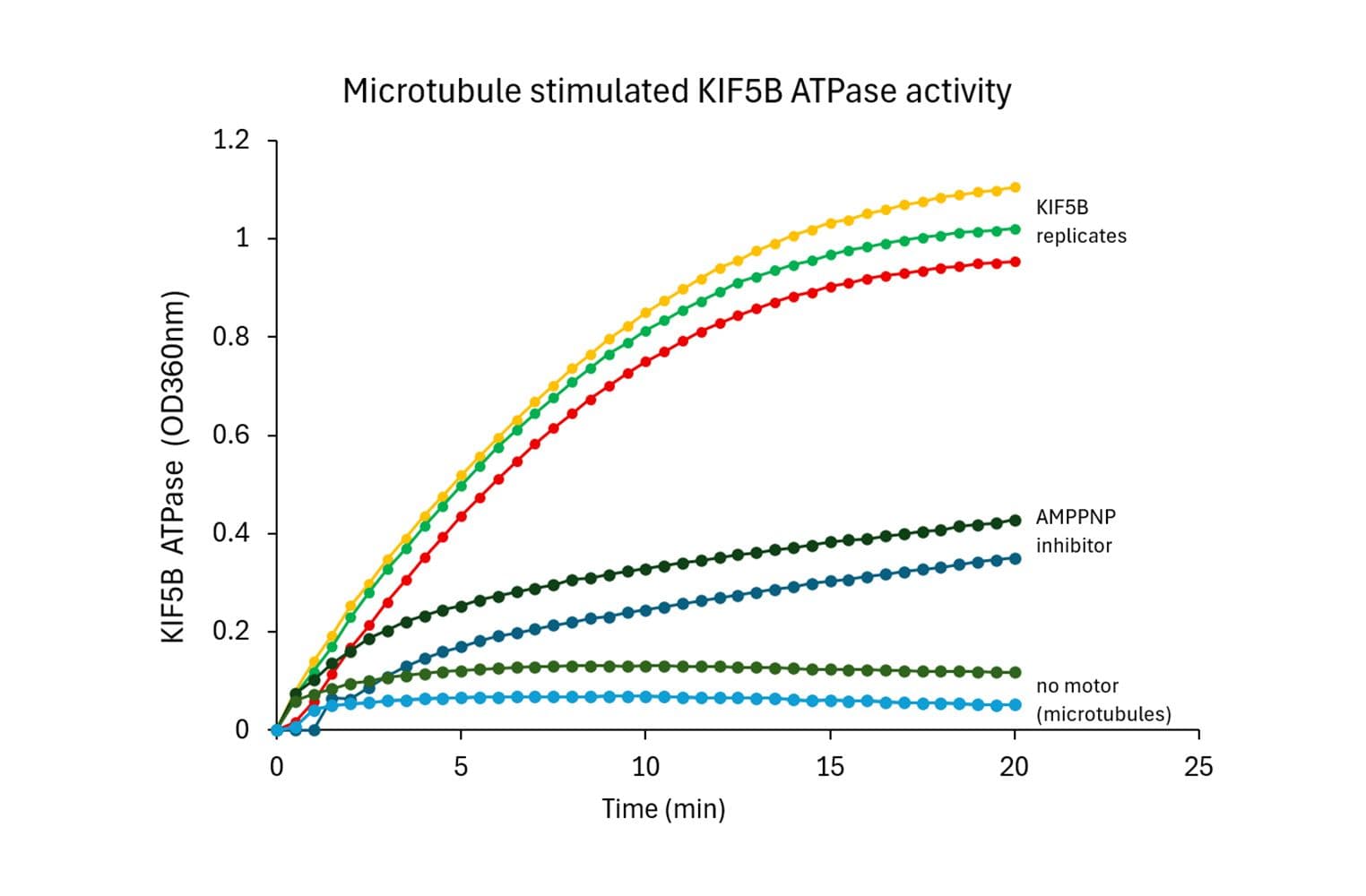
Biological activity of KIF5B is measured using a microtubule-activated ATPase assay. Under the conditions stated (see datasheet), KIF5B exhibits a microtubule-stimulated ATPase activity with a Vmax of ≥ 3500 nmol of ATP produced per minute per mg of KIF5B.
Cat. #KR01


