Modulator proteins
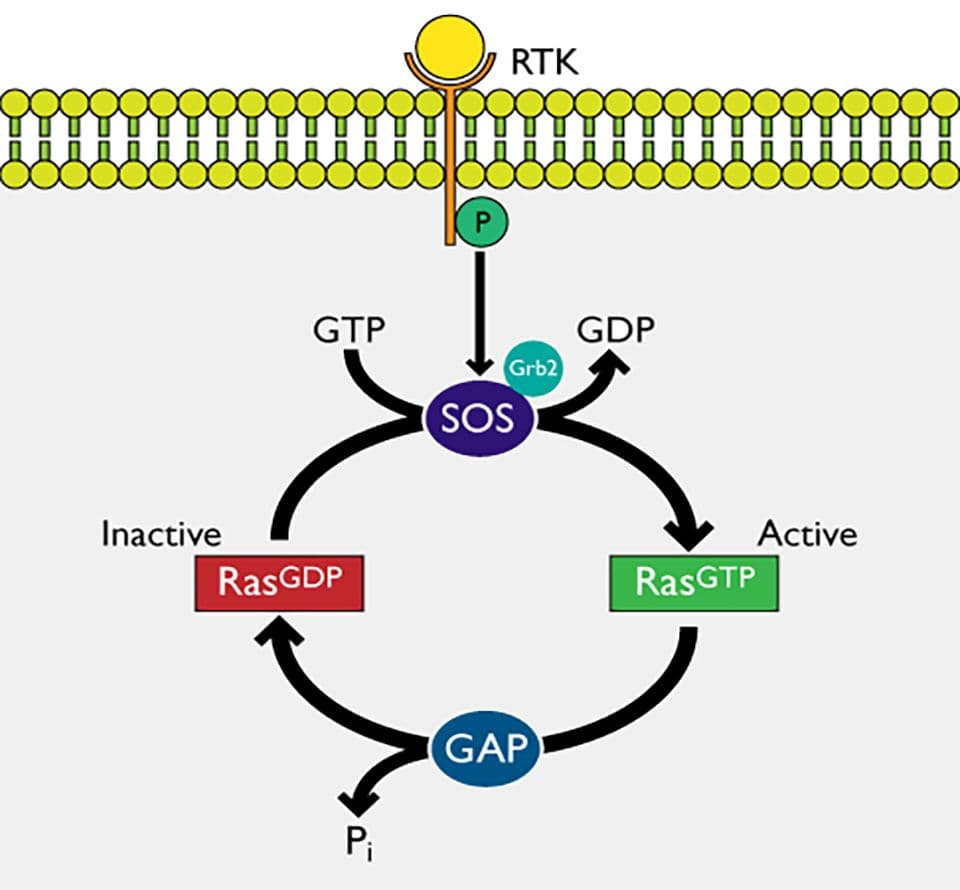
Small G-proteins are molecular switches that regulate numerous cellular processes. Three major classes of regulatory proteins tightly modulate their activity:
- Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors (GEFs) – Activate small GTPases by promoting the exchange of GDP for GTP.
- GTPase-Activating Proteins (GAPs) – Inactivate GTPases by accelerating the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP.
- Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitors (GDIs) – Maintain GTPases in their inactive GDP-bound state by preventing the dissociation of GDP.
Cyto provides a comprehensive portfolio of GTPase modulators such as Vav and SOS for in vitro applications.
Small G-proteins are molecular switches that regulate numerous cellular processes. Three major classes of regulatory proteins tightly modulate their activity:
- Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors (GEFs) – Activate small GTPases by promoting the exchange of GDP for GTP.
- GTPase-Activating Proteins (GAPs) – Inactivate GTPases by accelerating the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP.
- Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitors (GDIs) – Maintain GTPases in their inactive GDP-bound state by preventing the dissociation of GDP.
Cyto provides a comprehensive portfolio of GTPase modulators such as Vav and SOS for in vitro applications.