Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) protein has been produced in a bacterial expression system.;
Protein purity is assessed by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue-stained protein on a 4-20% polyacrylamide gel. Purity was determined to be ≥90% pure.
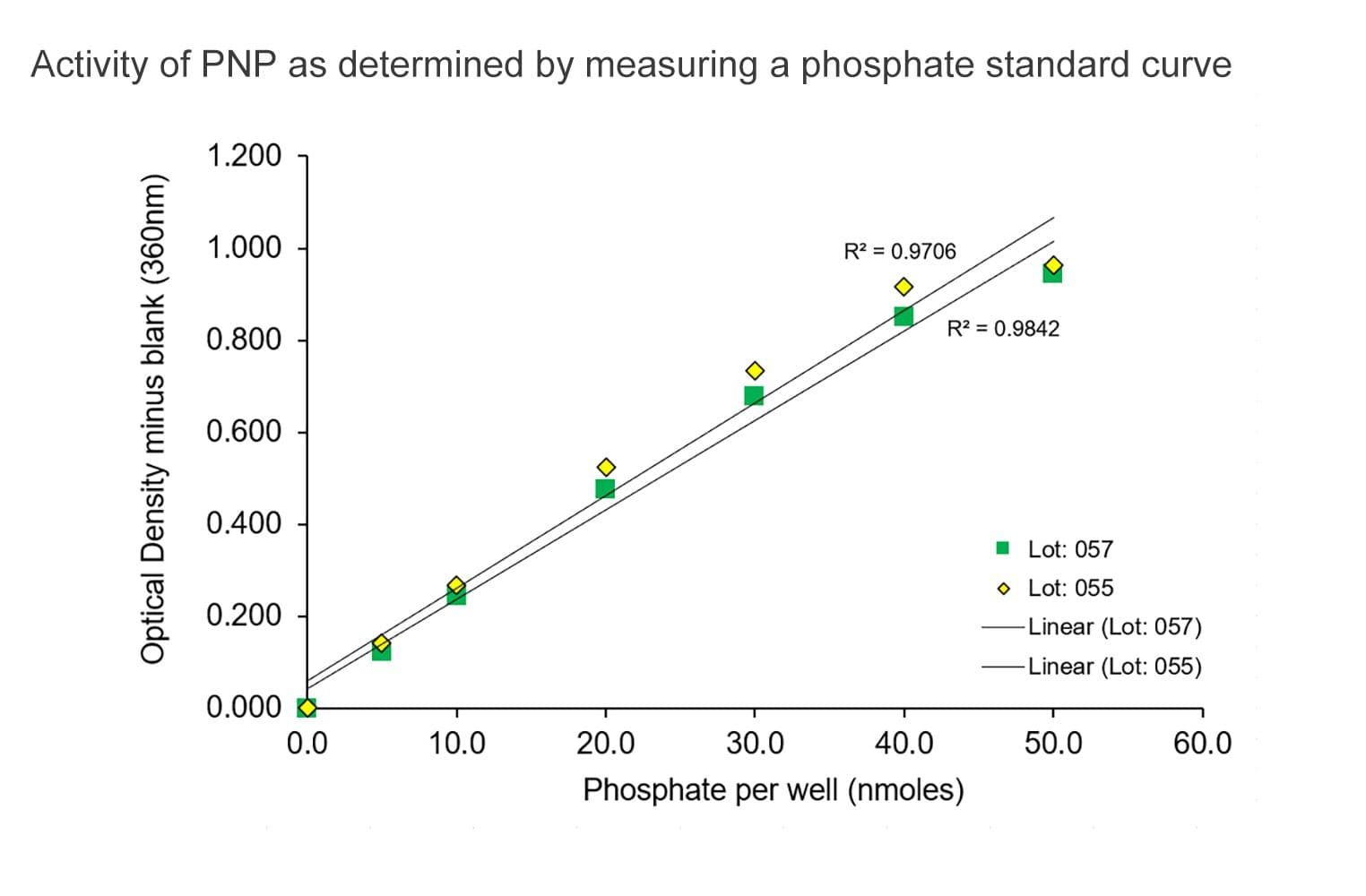
The biological activity of ELP03 is determined through the generation of a standard Pi curve. Under the experimental conditions, ELP03 can detect down to 3 nmol of Pi and is linear from 3-50 nmol (see datasheet).
The assay is based upon an absorbance shift (330 nm— 360 nm) that occurs when PNP catalytically converts 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine ribonucleoside (MESG) to 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine in the presence of inorganic phosphate (Pi). One molecule of Pi will yield one molecule of 2-amino-6-mercapto-7-methylpurine in an essentially irreversible reaction. Hence, in the presence of an ATPase or GTPase generating phosphate, the absorbance at 360 nm is directly proportional to the amount of Pi generated in an enzyme reaction.
Cat. #ELP03