Vav1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that regulates the activation of Rho family GTPases, playing a key role in cytoskeletal reorganization, cell signaling, and immune cell activation. Its activity is tightly controlled by phosphorylation, ensuring precise modulation of processes such as T-cell receptor signaling and immune responses.
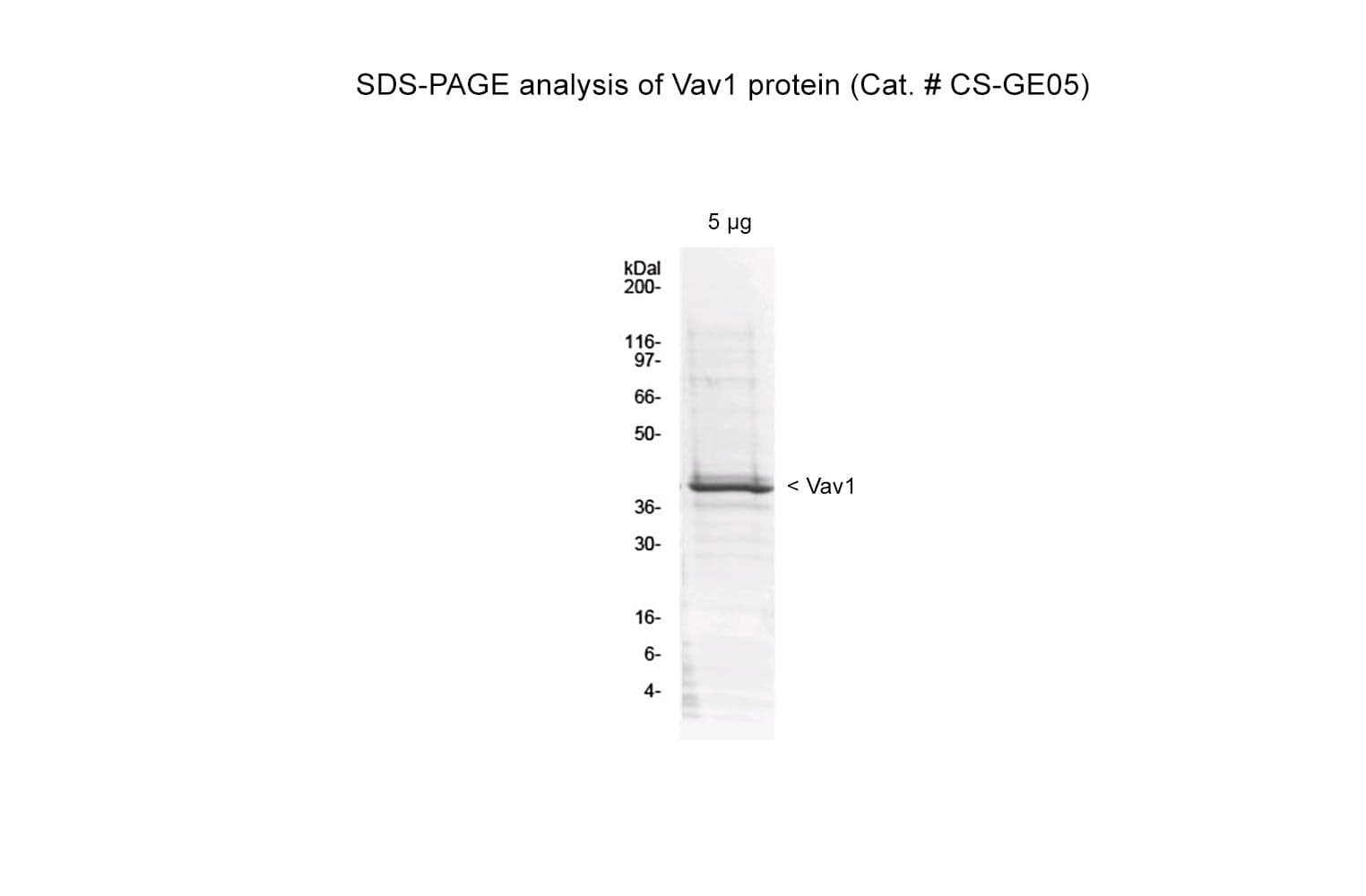
The DHPHC1 domain of human Vav1 protein (amino acids 168-522, Y174D) has been produced in a bacterial expression system. It contains a mutated amino acid (Y174D mutant) that mimics tyrosine phosphorylation, which is required for interaction with Rac1in vivo and in full-length Vav1. It is also 6xHis tagged at its amino terminus for purification purposes. The fusion protein has a molecular weight of 41 kDa, it is supplied as a lyophilized protein.
Protein purity is assessed using scanning densitometry of Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels. CS-GE05 is ≥80% pure
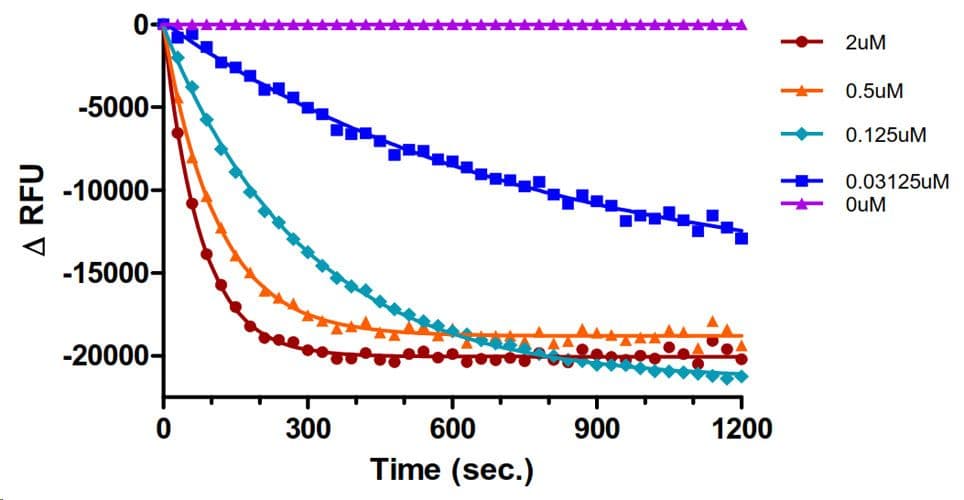
The biological activity of CS-GE05 is determined using an in vitro GEF assay. Under the experimental conditions (see datasheet), CS-GE05 increases Rac1 GTP exchange by ≥5 fold over intrinsic Rac exchange.
Cat. #CS-GE05