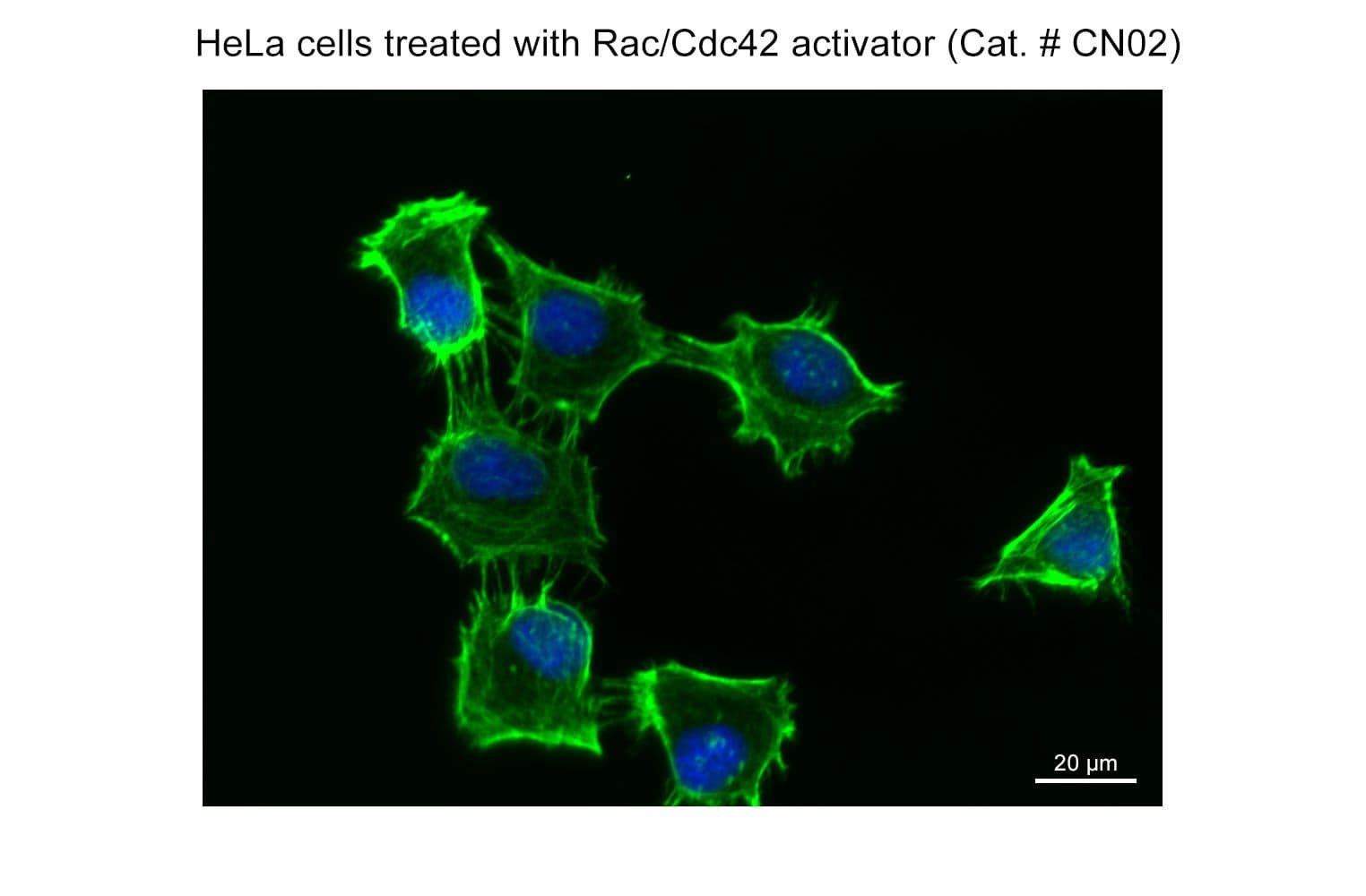
Part of the G-Switch™ line, CN02 (epidermal growth factor: EGF) acts through a tyrosine kinase receptor (EGFR) to rapidly stimulate actin reorganization through activation of Rac and/or Cdc42 small G-proteins. EGF is a valuable tool to study Rac/Cdc42 signaling pathways. It should be noted that EGF activates several other critical signal transduction pathways, including Ras/Raf/MAPK, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT, and data should be interpreted accordingly.
Preparation & Use:
≥98% by HPLC
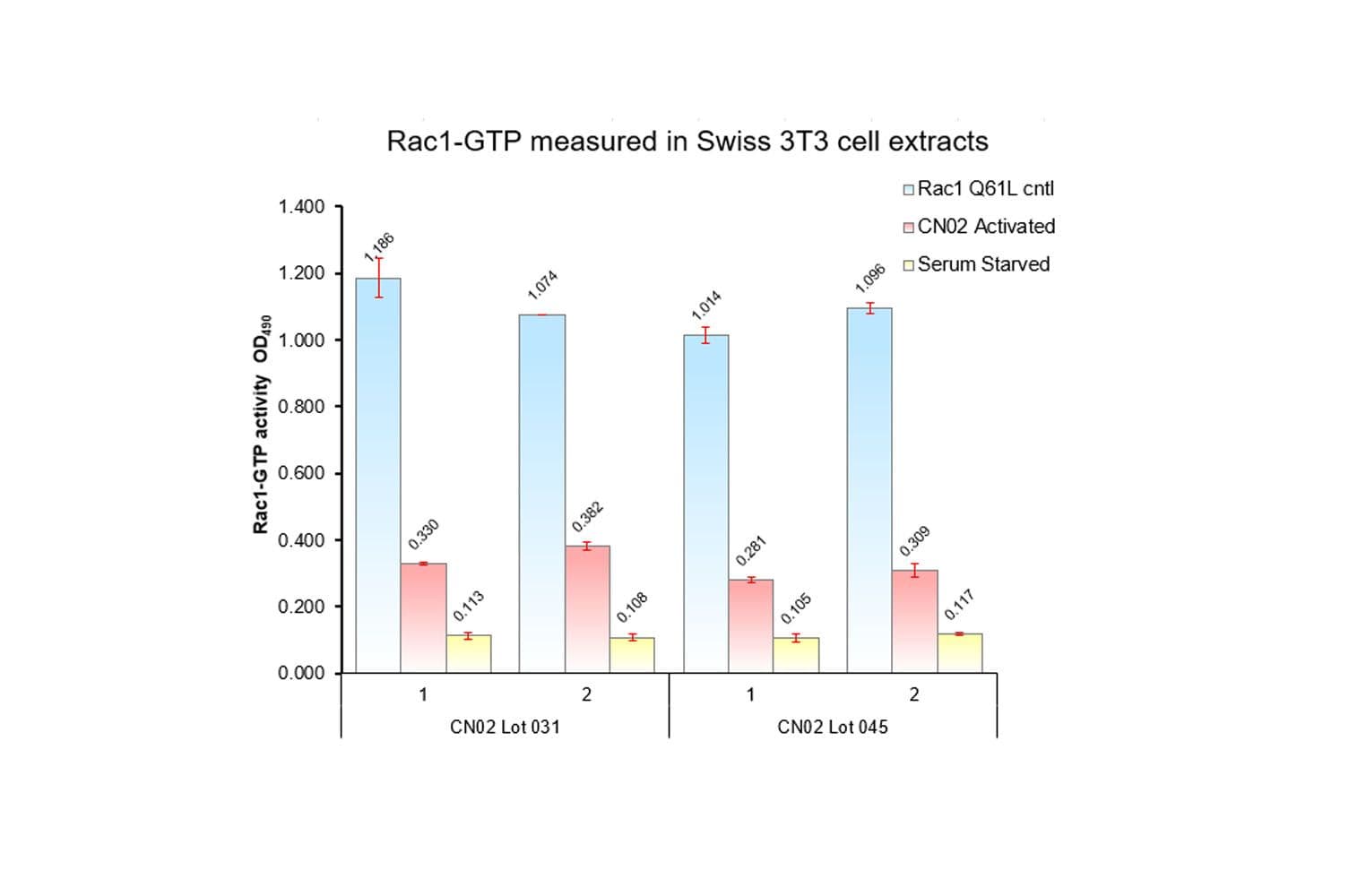
Biological activity of CN02 is demonstrated by its ability to activate Rac1 and Cdc42 in live Swiss 3T3 cells. Treatment at 1 unit/ml produces optimal activation, approximately twofold, within 1-2 minutes as measured by a Rac1BK128 and Cdc42 BK127 G-LISA assays. Responses to CN02 will vary depending on the cell line used.
Cat. #CN02

© 2026 Cytoskeleton, Inc All Rights Reserved.