Collection Overview
Cytoskeleton Inc. is proud to be a part of this excellent collection of protocols and methods.
The cytoskeleton and its associated molecular motors and binding proteins perform numerous cellular processes ranging from migration and division to mechanosensing; thus, enabling the cells to move, change shape, and grow. The cytoskeleton includes the semiflexible actin filaments, rigid microtubules, and intermediate filaments that provide structural and mechanical support to the cells; additionally, the cytoskeleton is also a quintessential example of active matter with potential materials applications ranging from wound healing and drug delivery to filtration and soft robotics. In an effort to understand these interactions and contributions from the different cytoskeletal constituents that lead to signature cellular properties, researchers have developed powerful in vitro reconstitution methods to build and study cytoskeleton systems outside the cells. However, due to the complexity and non-equilibrium nature of these systems, as well as the labile nature of their constituents, in vitro reconstitution methods are often difficult to replicate from lab to lab. This collection highlights the different reconstitution assays and experimental methods that researchers at the forefront of cytoskeleton research are using to recreate and elucidate cytoskeleton systems in an effort to advance biophysics and materials science alike.
Featured Methods:
Reconstituting and Characterizing Actin-Microtubule Composites with Tunable Motor-Driven Dynamics and Mechanics
Mehrzad Sasanpour1, Daisy H. Achiriloaie1,2, Gloria Lee1, Gregor Leech1, Maya Hendija1, K. Alice Lindsay3, Jennifer L. Ross3, Ryan J. McGorty1, Rae M. Robertson-Anderson11Department of Physics and Biophysics, University of San Diego, 2W. M. Keck Science Department, Scripps College, Pitzer College, and Claremont McKenna College, 3Department of Physics, Syracuse University
Abstract
The composite cytoskeleton, comprising interacting networks of semiflexible actin filaments and rigid microtubules, restructures and generates forces using motor proteins such as myosin II and kinesin to drive key processes such as migration, cytokinesis, adhesion, and mechanosensing. While actin-microtubule interactions are key to the cytoskeleton's versatility and adaptability, an understanding of their interplay with myosin and kinesin activity is still nascent. This work describes how to engineer tunable three-dimensional composite networks of co-entangled actin filaments and microtubules that undergo active restructuring and ballistic motion, driven by myosin II and kinesin motors, and are tuned by the relative concentrations of actin, microtubules, motor proteins, and passive crosslinkers. Protocols for fluorescence labeling of the microtubules and actin filaments to most effectively visualize composite restructuring and motion using multi-spectral confocal imaging are also detailed. Finally, the results of data analysis methods that can be used to quantitatively characterize non-equilibrium structure, dynamics, and mechanics are presented. Recreating and investigating this tunable biomimetic platform provides valuable insight into how coupled motor activity, composite mechanics, and filament dynamics can lead to myriad cellular processes from mitosis to polarization to mechano-sensation.
Featured Methods:
In Vitro Reconstitution of the Actin Cytoskeleton Inside Giant Unilamellar Vesicles
Sheng Chen1, Zachary Gao Sun2,3, Michael P. Murrell1,2,31Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yale University, 2Systems Biology Institute, Yale University, 3Department of Physics, Yale University
Abstract
The actin cytoskeleton, the principal mechanical machinery in the cell, mediates numerous essential physical cellular activities, including cell deformation, division, migration, and adhesion. However, studying the dynamics and structure of the actin network in vivo is complicated by the biochemical and genetic regulation within live cells. To build a minimal model devoid of intracellular biochemical regulation, actin is encapsulated inside giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs, also called liposomes). The biomimetic liposomes are cell-sized and facilitate a quantitative insight into the mechanical and dynamical properties of the cytoskeleton network, opening a viable route for bottom-up synthetic biology. To generate liposomes for encapsulation, the inverted emulsion method (also referred to as the emulsion transfer method) is utilized, which is one of the most successful techniques for encapsulating complex solutions into liposomes to prepare various cell-mimicking systems. With this method, a mixture of proteins of interest is added to the inner buffer, which is later emulsified in a phospholipid-containing mineral oil solution to form monolayer lipid droplets. The desired liposomes are generated from monolayer lipid droplets crossing a lipid/oil-water interface. This method enables the encapsulation of concentrated actin polymers into the liposomes with desired lipid components, paving the way for in vitro reconstitution of a biomimicking cytoskeleton network.
Featured Methods:
Self-Assembly of Microtubule Tactoids
Prashali Chauhan1, Sumon Sahu1,2, Niaz Goodbee1, Sophia Martin1, Hong Beom Lee1, Ruell Branch1, Jennifer M. Schwarz1, Jennifer L. Ross11Physics Department, Syracuse University, 2Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale School of Medicine
Abstract
The cytoskeleton is responsible for major internal organization and re-organization within the cell, all without a manager to direct the changes. This is especially the case during mitosis or meiosis, where the microtubules form the spindle during cell division. The spindle is the machinery used to segregate genetic material during cell division. Toward creating self-organized spindles in vitro, we recently developed a technique to reconstitute microtubules into spindle-like assemblies with a minimal set of microtubule-associated proteins and crowding agents. Specifically, MAP65 was used, which is an antiparallel microtubule crosslinker from plants, a homolog of Ase1 from yeast and PRC1 from mammalian organisms. This crosslinker self-organizes microtubules into long, thin, spindle-like microtubule self-organized assemblies. These assemblies are also similar to liquid crystal tactoids, and microtubules could be used as mesoscale mesogens. Here, protocols are presented for creating these microtubule tactoids, as well as for characterizing the shape of the assemblies using fluorescence microscopy and the mobility of the constituents using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching.
See These Tools In Action - Citation Spotlights
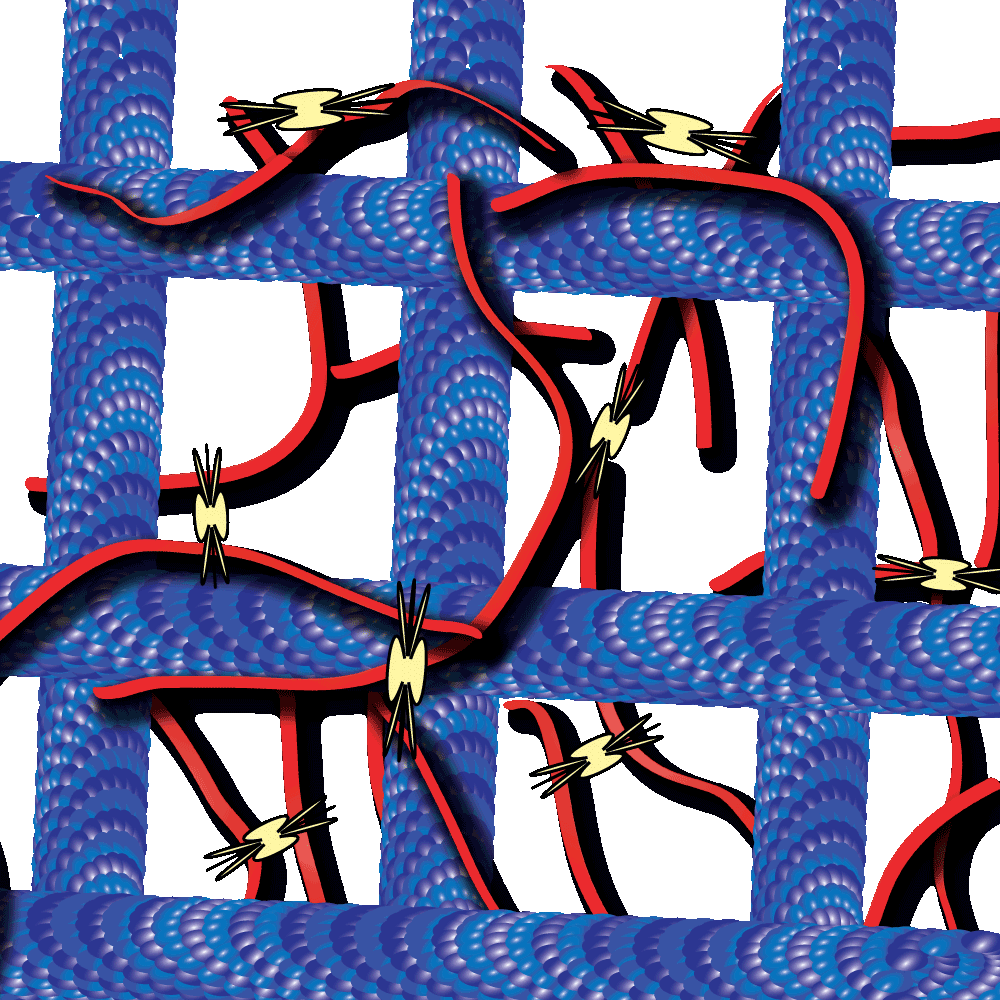
Cytoskeleton proteins, actin and tubulin, are two of the most well-characterized proteins and the networks they form have been actively studied over the past decade. Interestingly, these actin and tubulin networks interact extensively in cells, yet our understanding of how these networks affect the other’s dynamics is just beginning to come to light. Work by Dr. Ross and Dr. Robertson-Anderson has led the way towards unmasking this mystery. In their recent study these groups sought to determine how the interactions between actin and microtubule networks impact actomyosin activity. They utilized cutting-edge technologies like particle image velocimetry and dynamic differential microscopy to measure the network dynamics of actin and microtubules that are co-entangled in the presence of myosin II. Interestingly they observed that microtubules facilitated organized contraction of actomyosin networks that were otherwise disjointed and displayed disordered dynamics. Importantly, they also observed that these co-entangled networks can undergo ballistic contraction with indistinguishable characteristics.
Please visit our product pages for product specific citations
99% Pure Tubulin Protein - Tubulin Polymerization Assay - Pre-Formed Microtubules
Cytoskeleton's line of Tubulin Tools
Tubulin Tools Brochure
Cytoskeleton Inc. was the first company to offer biologically active tubulin proteins, kits and reagents for the scientific community. Click through this brochure or the button below to see a sample of Cytoskeleton's Tubulin Tools