Cardiac myosin is a specialized motor protein that drives heart muscle contraction by converting chemical energy from ATP into mechanical force. Modulation of cardiac myosin activity is an active area of therapeutic interest.
Cardiac Heavy Meromyosin (HMM fragment) is prepared by digesting cardiac myosin MY03 with -chymotrypsin in the presence of MgCl2 to liberate the soluble HMM. A final polishing step using anionic exchange chromatography is performed.
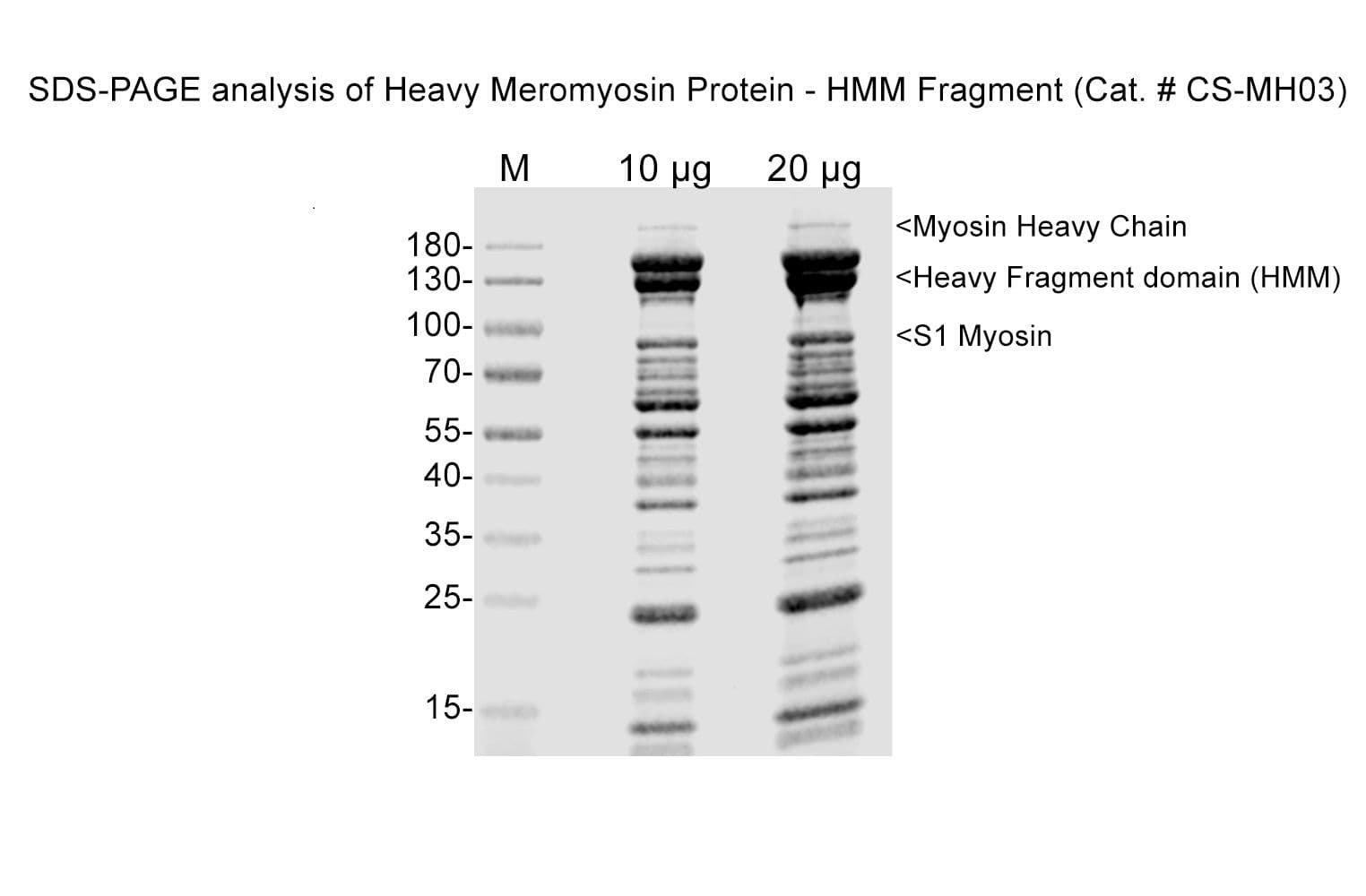
Protein purity is assessed by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue-stained protein on a 4-20% polyacrylamide gel. Purity is determined to be >90% pure HMM and <1% contaminating S1 fragment.
The biological activity of the bovine cardiac myosin HMM fragment is measured by its rate of F-actin–activated ATP hydrolysis. Under the specified experimental conditions (see datasheet), the presence of F-actin increases the HMM ATPase rate by more than fivefold compared to HMM alone. The observed specific activity falls within published values of 50–100 nmol/min/mg, equivalent to approximately 1.0–2.0 ATP molecules hydrolyzed per myosin head per second.
Cat. #CS-MH03