+3
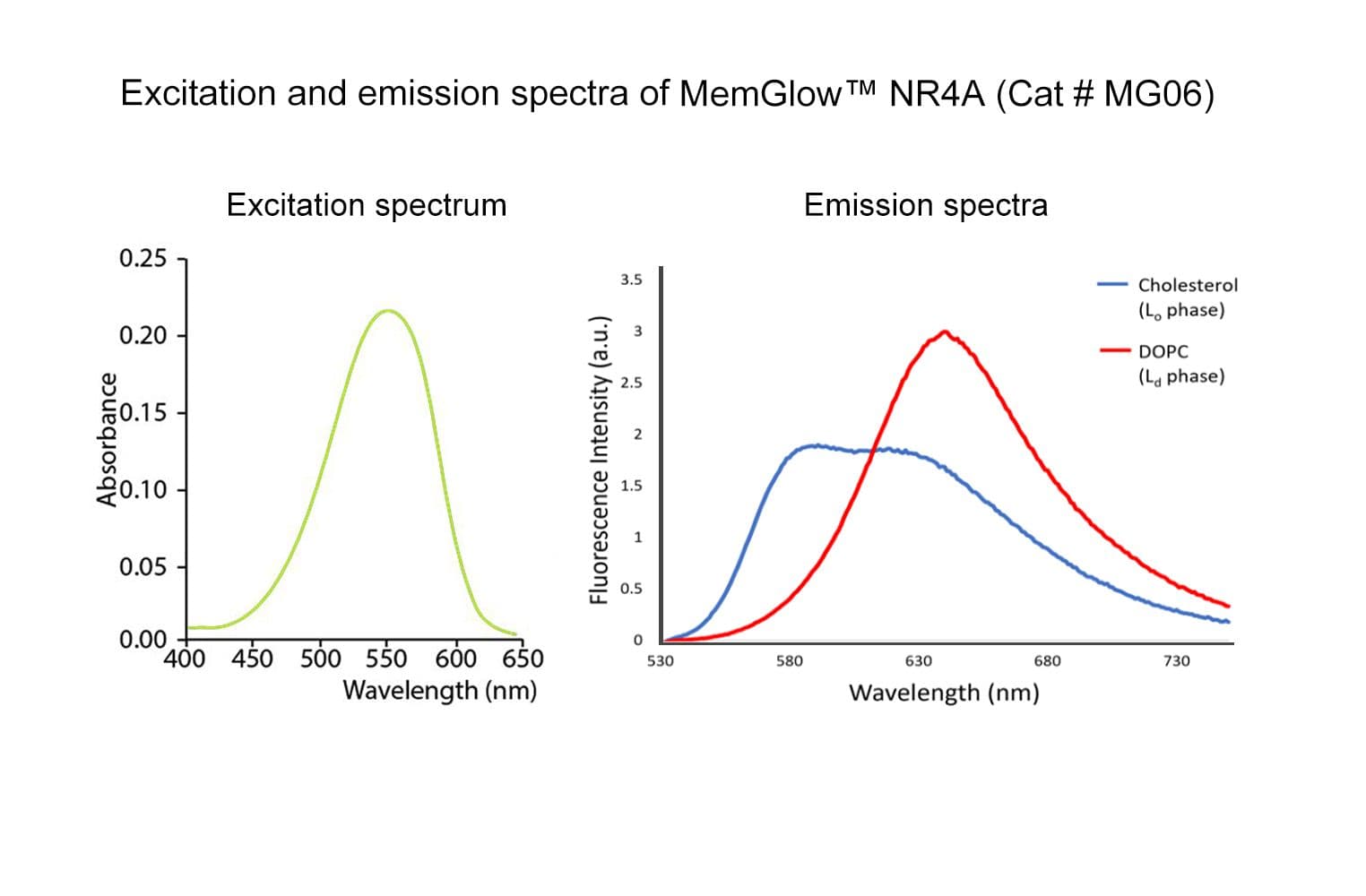
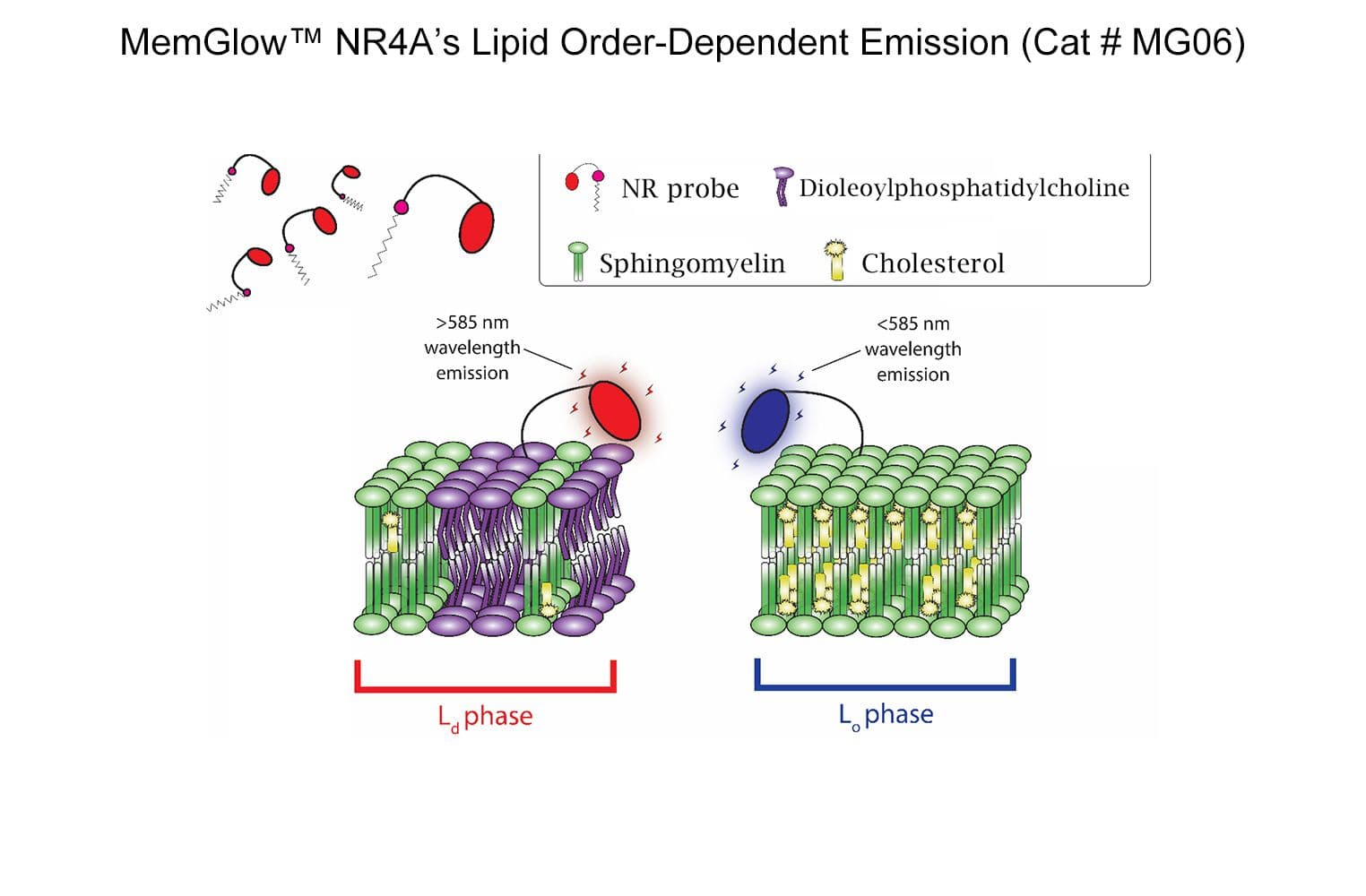
MemGlow™NR4A is a solvatchromic probe that changes its emission spectra in response to a change in membrane (solvent) polarity. The probe acts like an on/off switch that has been optimized for Super Resolution Point Accumulation for Imaging in Nanoscale Topography (SR-PAINT). Upon binding with a plasma membrane in a predominant liquid ordered (LO) phase, NR4A exhibits a 45-50 nm wavelength shift relative to the liquid disordered (Ld) phase, enabling investigators to examine the nanoscale distribution of local chemical polarity in plasma membranes.
Key features
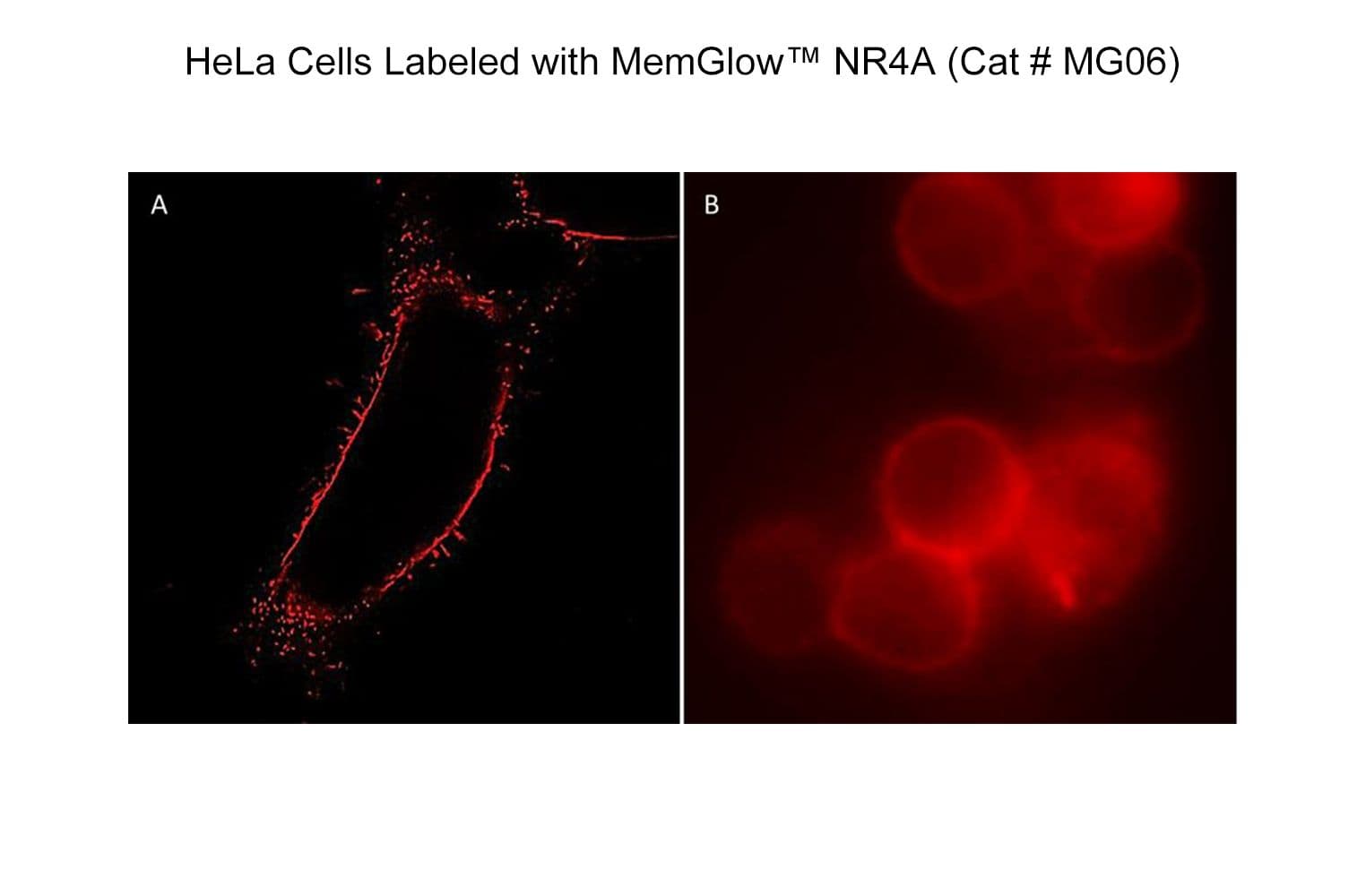
The biological activity of MG06 is assessed by the ability of the probe to efficiently label plasma membranes in live HEK293 cell culture.
Cat. #MG06