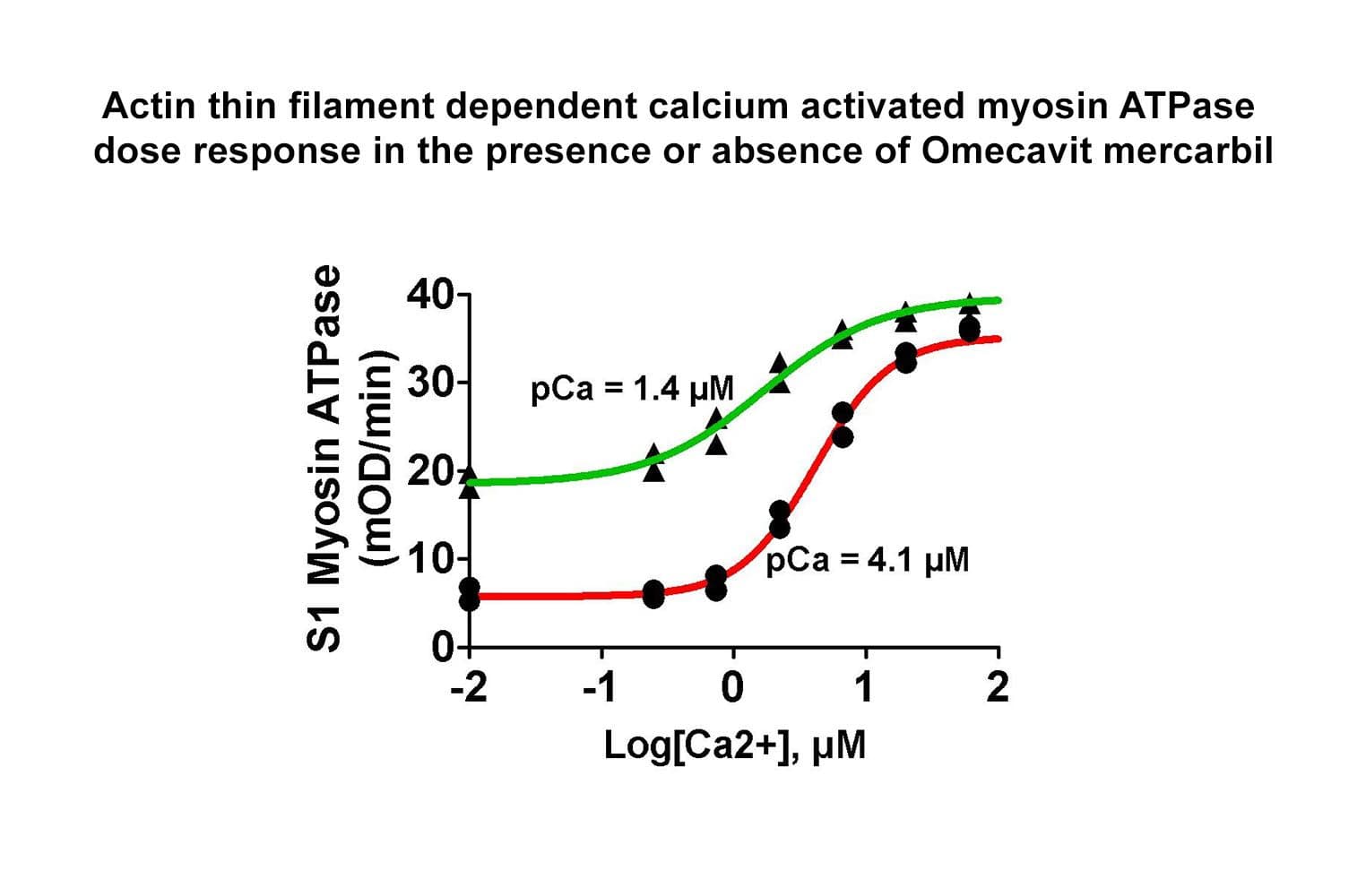
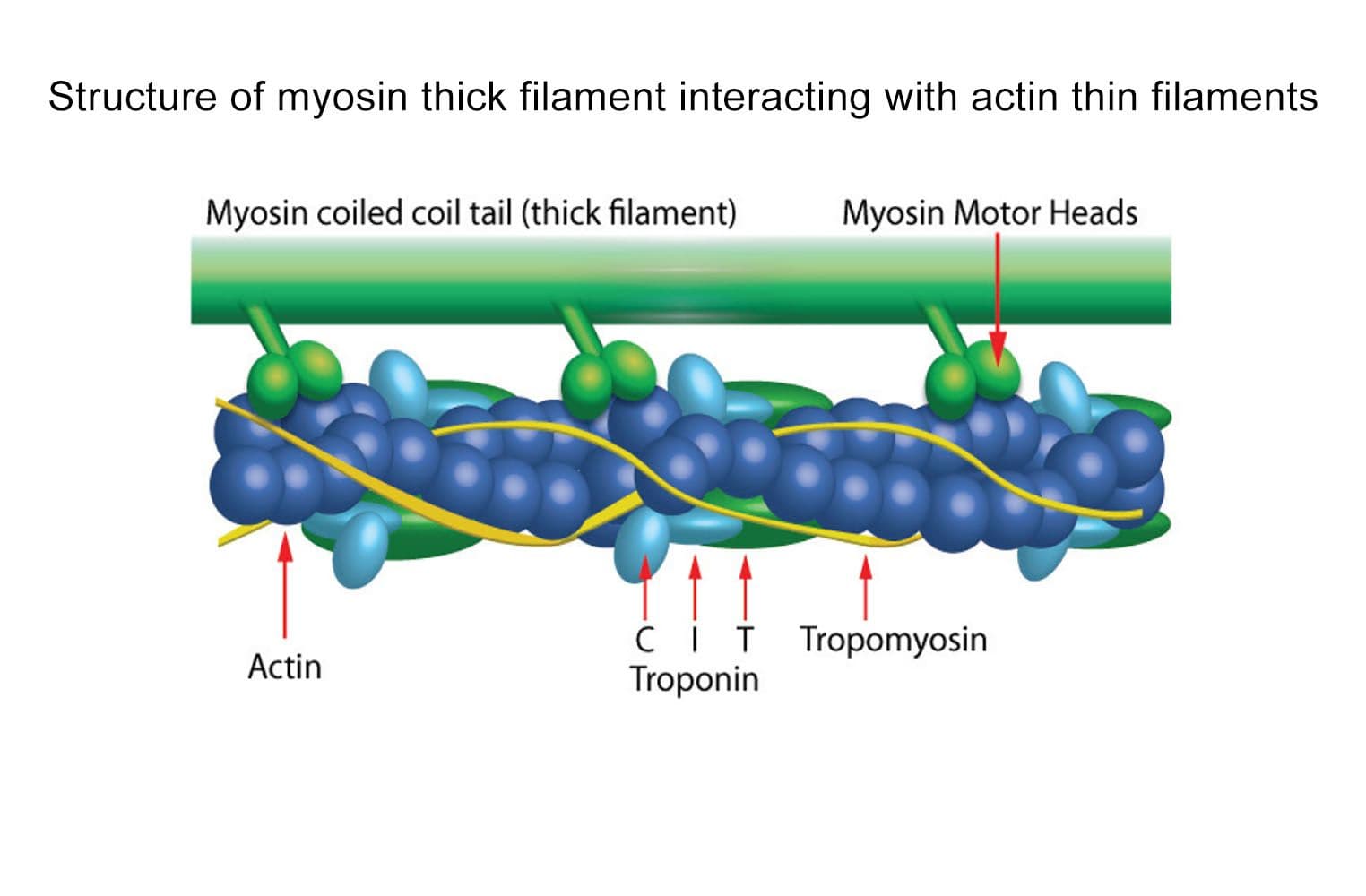
Cardiac myosin is a specialized motor protein that drives heart muscle contraction by converting chemical energy from ATP into mechanical force. Modulation of cardiac myosin activity is an active area of therapeutic interest. The myosin S1 fragment, which retains high enzymatic activity, is widely used in F-actin or actin thin filament ATPase assays. These assays are valuable tools in drug discovery for screening compounds that can alter myosin activity.
Cardiac myosin S1 fragment is prepared by digesting cardiac myosin MY03 with -chymotrypsin in the presence of EDTA to liberate the soluble S1 fragment.
Cardiac myosin S1 fragment is produced from cardiac muscle myosin that is ≥90% pure MY03.
The purified myosin S1 fragment remains biologically active in a calcium-stimulated ATPase assay using a soluble sarcomere system (see datasheet). Briefly, the cardiac thin filament complex (CTFC) is assembled to mimic muscle thin filaments. Myosin S1 fragment is added in sub-stoichiometric amounts, and ATP with calcium initiates the reaction. Quality controls ensure that in the absence of calcium, CTFC blocks myosin ATPase; the addition of 10 μM calcium relieves inhibition by disrupting the CTFC, allowing myosin–actin interaction and ATPase activation.
Cat. #CS-MYS03