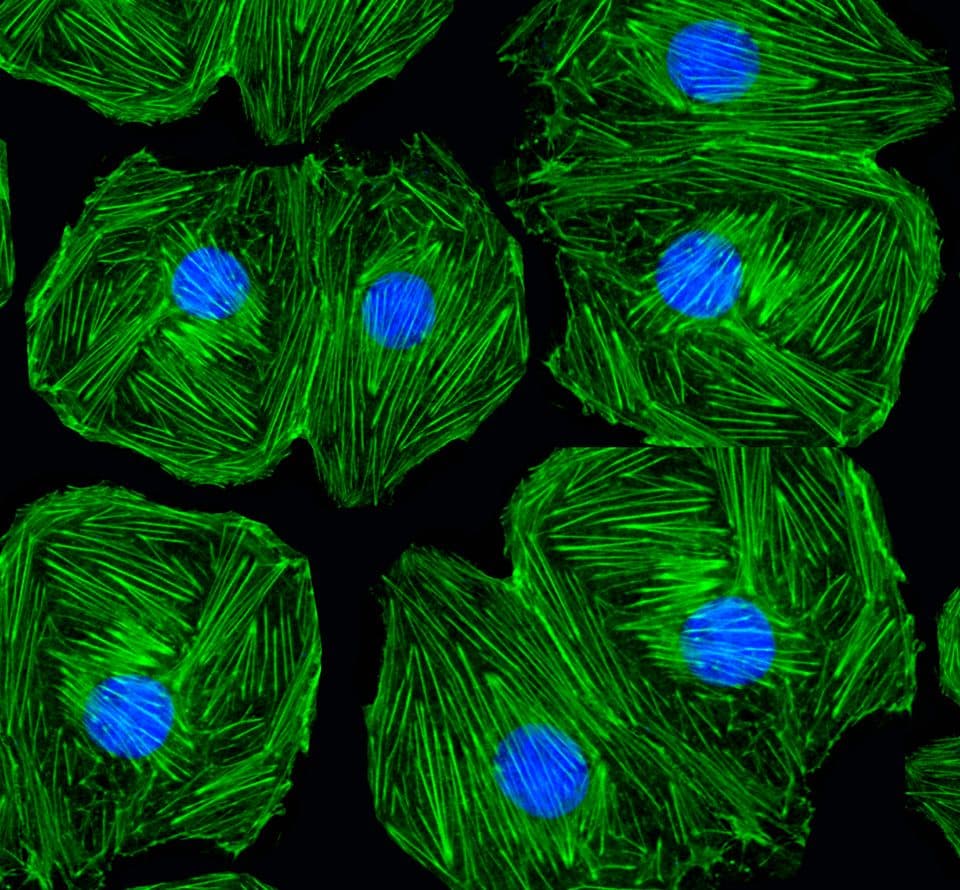
Acti-stain™ fluorescent phalloidins
Phalloidin conjugates are commonly used in fluorescence imaging to selectively stain F-actin across a range of sample types, including fixed cells, tissue sections, and cell-free systems.
Key Highlights
- Available conjugates to cover a wide spectral range
- Compatible with popular filter sets such as FITC, TRITC and Cy 5
- Provides enough reagent for 70 ml of working solution
- Manufactured in-house under stringent quality control for reliable, reproducible results
Trust our phalloidin conjugates to deliver bright, dependable F-actin staining that enhances the quality and clarity of your imaging experiments every time.
Phalloidin conjugates are commonly used in fluorescence imaging to selectively stain F-actin across a range of sample types, including fixed cells, tissue sections, and cell-free systems.
Key Highlights
- Available conjugates to cover a wide spectral range
- Compatible with popular filter sets such as FITC, TRITC and Cy 5
- Provides enough reagent for 70 ml of working solution
- Manufactured in-house under stringent quality control for reliable, reproducible results
Trust our phalloidin conjugates to deliver bright, dependable F-actin staining that enhances the quality and clarity of your imaging experiments every time.