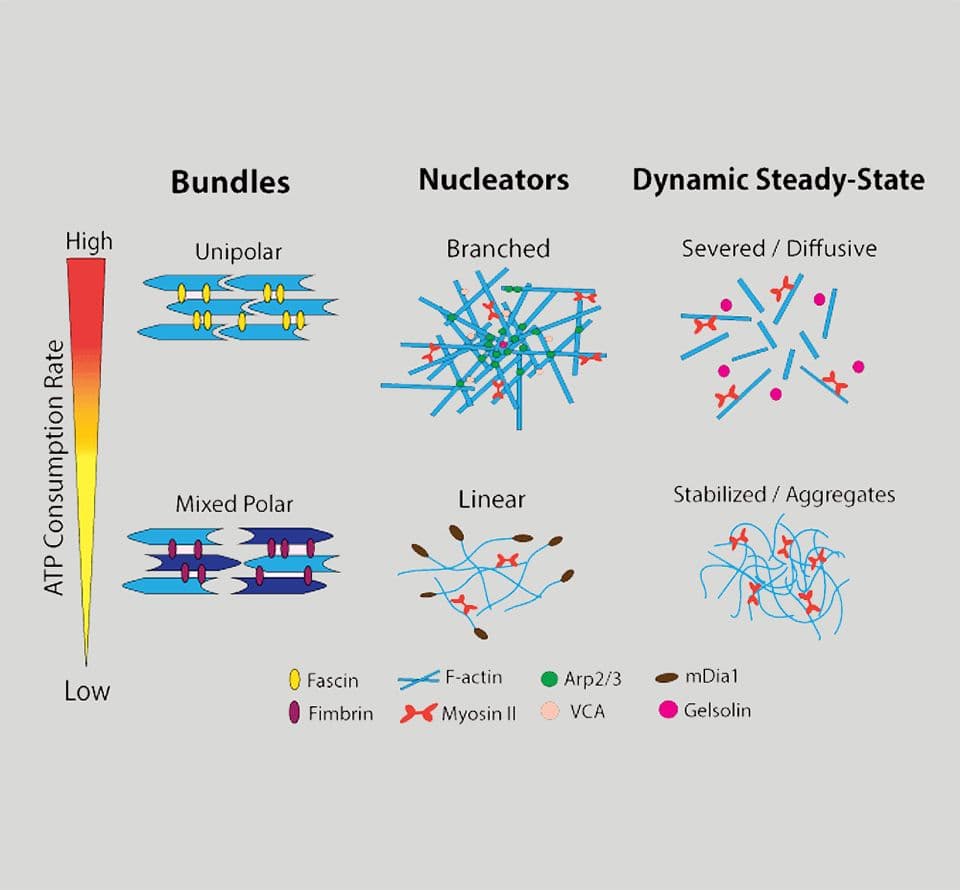
Actin-binding proteins (ABPs)
Actin-binding proteins (ABPs) are essential actin cytoskeleton regulators, driving complex cellular behaviors such as motility, division, and shape maintenance. These proteins often serve multiple regulatory functions depending on the cellular context, making them versatile tools for dissecting actin dynamics.
Cyto is proud to offer a comprehensive portfolio of pure, biologically active, and extensively cited ABPs trusted by researchers worldwide. Our proteins are optimized for purity, activity, and reproducibility in demanding experimental systems.
Explore Our Functional Categories:
- Capping Proteins
Examples: Gelsolin, Arp2/3
Regulate filament length by binding to the barbed ends of actin filaments, controlling polymerization and filament turnover. - Nucleating Proteins
Example: Arp2/3
Complex Induce the formation of new actin branches, promoting the development of branched filament networks for lamellipodial protrusion and intracellular trafficking. - Bundling Proteins
Example: Alpha-actinin
Crosslink parallel actin filaments to stabilize cytoskeletal structures like stress fibers and focal adhesions. - Severing Proteins
Examples: Cofilin, Gelsolin
Enhance actin dynamics by severing F-actin, promoting filament disassembly and turnover for rapid remodeling. - Sequestering Proteins
Example: Profilin
Binds G-actin to regulate monomer availability, maintaining a pool of polymerizable actin and modulating filament growth. - Motor Proteins
Example: Myosins
Convert ATP into mechanical force, driving vesicle transport, tension generation, and organelle positioning along actin tracks. - F-actin Binding Proteins
Example: Mical
Oxidizes and depolymerizes F-actin upon activation, a critical mechanism in axonal guidance and cell morphology regulation.
Whether you're mapping signaling pathways, engineering cell motility, or dissecting cytoskeletal mechanics, Cyto's ABP collection equips you with the tools to reveal new cellular insights.
Actin-binding proteins (ABPs) are essential actin cytoskeleton regulators, driving complex cellular behaviors such as motility, division, and shape maintenance. These proteins often serve multiple regulatory functions depending on the cellular context, making them versatile tools for dissecting actin dynamics.
Cyto is proud to offer a comprehensive portfolio of pure, biologically active, and extensively cited ABPs trusted by researchers worldwide. Our proteins are optimized for purity, activity, and reproducibility in demanding experimental systems.
Explore Our Functional Categories:
- Capping Proteins
Examples: Gelsolin, Arp2/3
Regulate filament length by binding to the barbed ends of actin filaments, controlling polymerization and filament turnover. - Nucleating Proteins
Example: Arp2/3
Complex Induce the formation of new actin branches, promoting the development of branched filament networks for lamellipodial protrusion and intracellular trafficking. - Bundling Proteins
Example: Alpha-actinin
Crosslink parallel actin filaments to stabilize cytoskeletal structures like stress fibers and focal adhesions. - Severing Proteins
Examples: Cofilin, Gelsolin
Enhance actin dynamics by severing F-actin, promoting filament disassembly and turnover for rapid remodeling. - Sequestering Proteins
Example: Profilin
Binds G-actin to regulate monomer availability, maintaining a pool of polymerizable actin and modulating filament growth. - Motor Proteins
Example: Myosins
Convert ATP into mechanical force, driving vesicle transport, tension generation, and organelle positioning along actin tracks. - F-actin Binding Proteins
Example: Mical
Oxidizes and depolymerizes F-actin upon activation, a critical mechanism in axonal guidance and cell morphology regulation.
Whether you're mapping signaling pathways, engineering cell motility, or dissecting cytoskeletal mechanics, Cyto's ABP collection equips you with the tools to reveal new cellular insights.