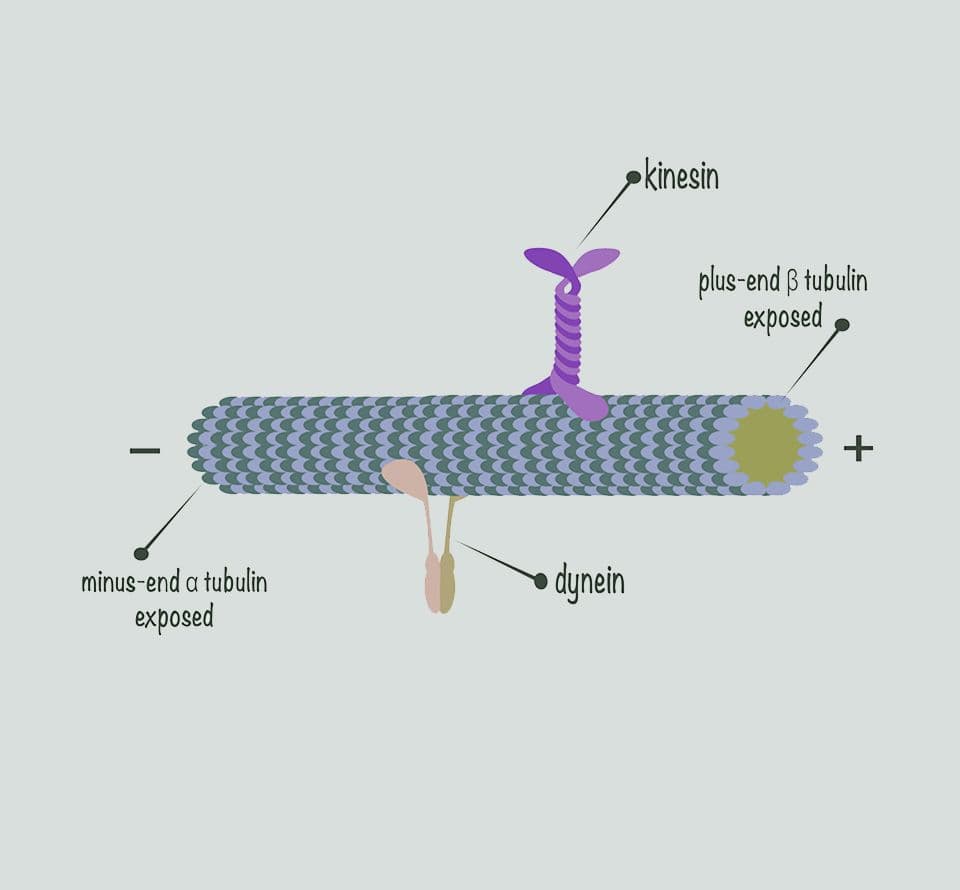
Cytoskeleton motor protein reagents
Advance your motor protein research with reagents trusted worldwide for over 30 years. Cyto delivers high-purity cytoskeletal motor proteins and kits with proven biological activity and reproducibility. Every lot is rigorously validated for publication-ready results, backed by expert support to help you move forward confidently.