Tubulin is purified from porcine brain using a modified Shelanski et al. method. The resulting protein contains approximately 97% tubulin and 3% microtubule associated proteins. Supplied as a lyophilized powder. Shipped at ambient temperature, powder stored at 4°C.
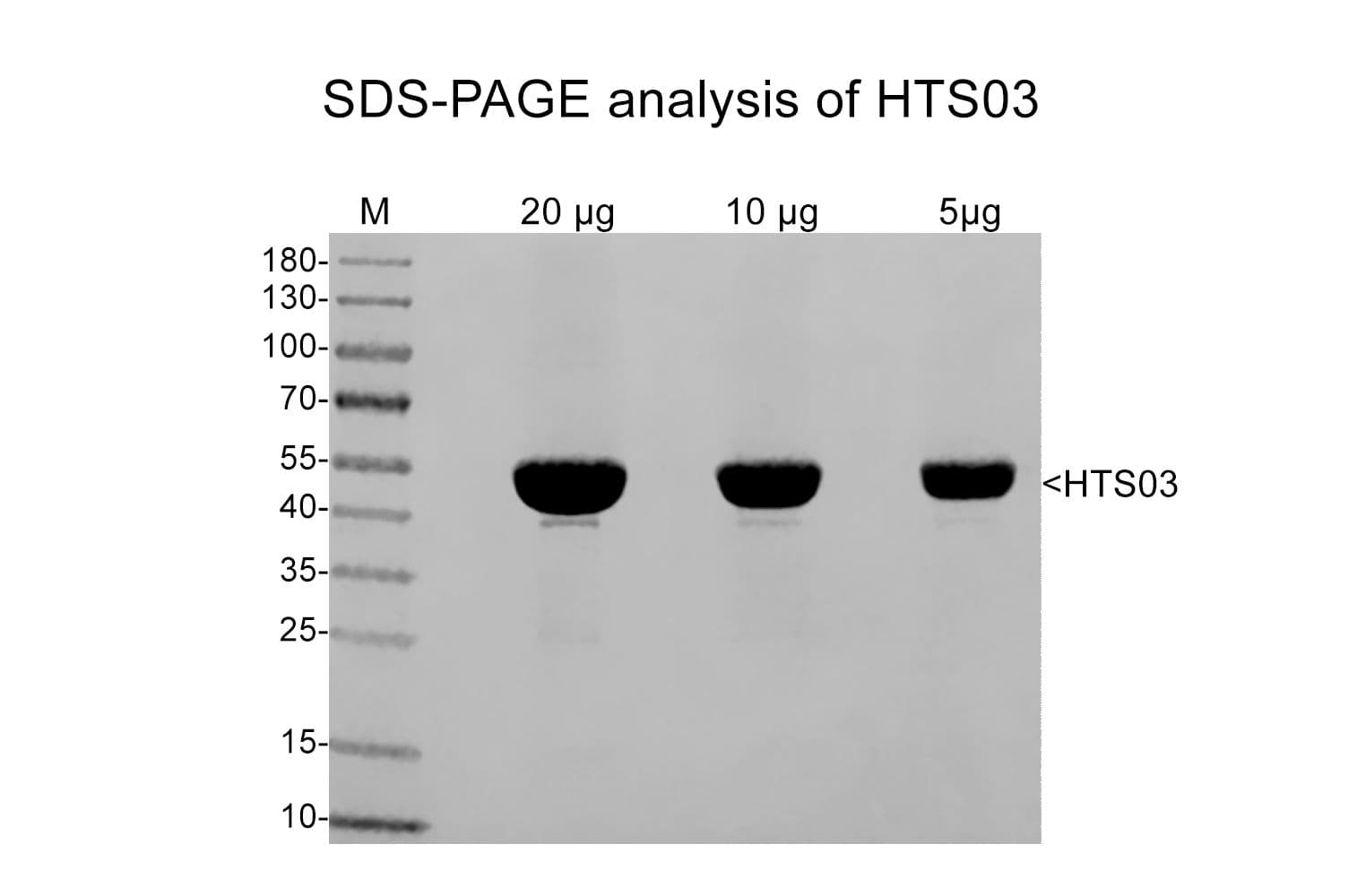
Tubulin is a heterodimer of α- and β-isotypes, each 55 kDa. SDS-PAGE shows a single 55 kDa band. The molecular weight of the functional heterodimer is 110 kDa. MAPs vary in molecular weight and include MAP1/2 (~250 kDa) and Tau isoforms (~37-44 kDa)
Protein purity is assessed by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on a12% polyacrylamide gel. Purity is determined to be ~97% tubulin and ~3% microtubule associated protein (MAP).
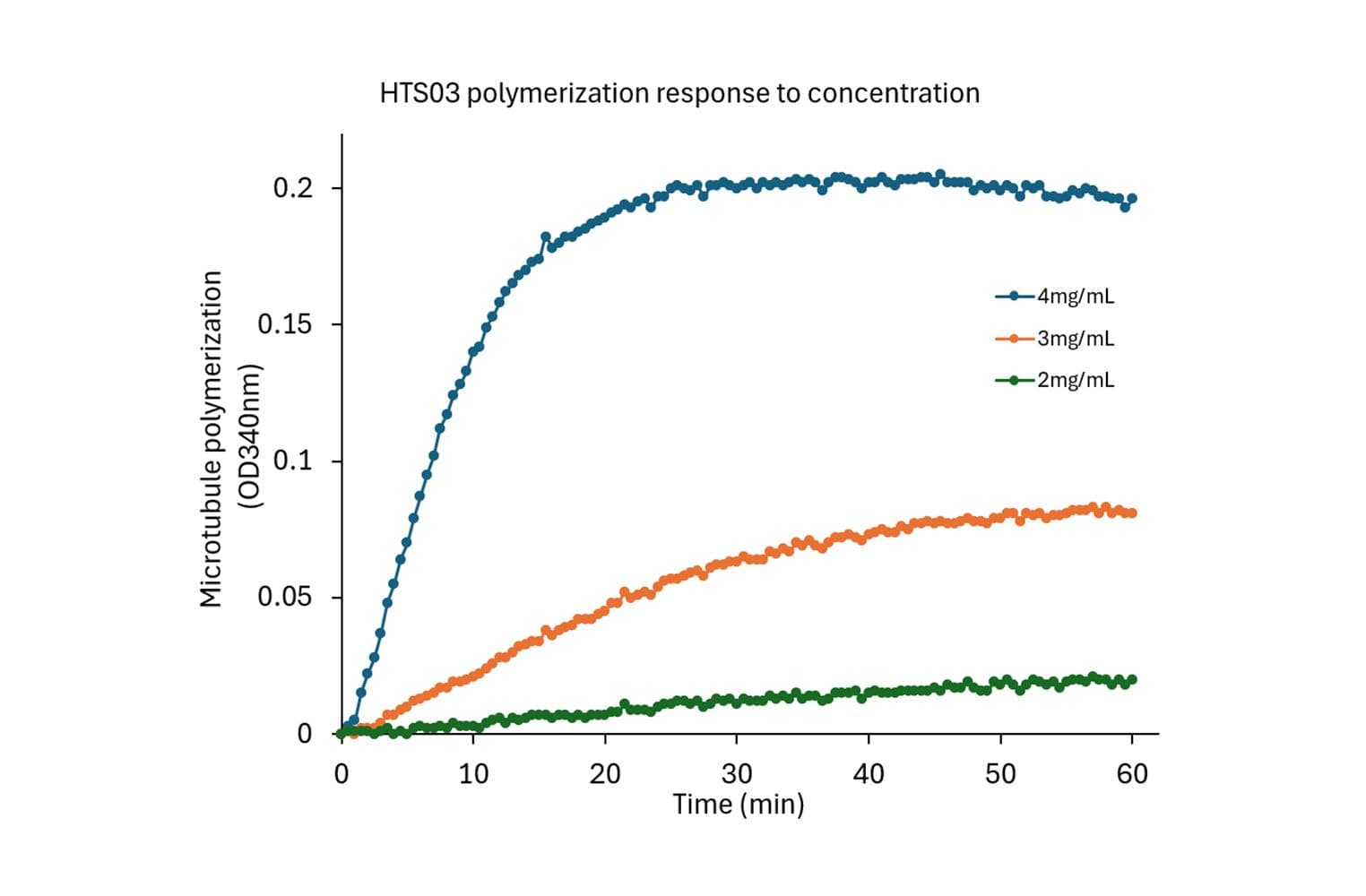
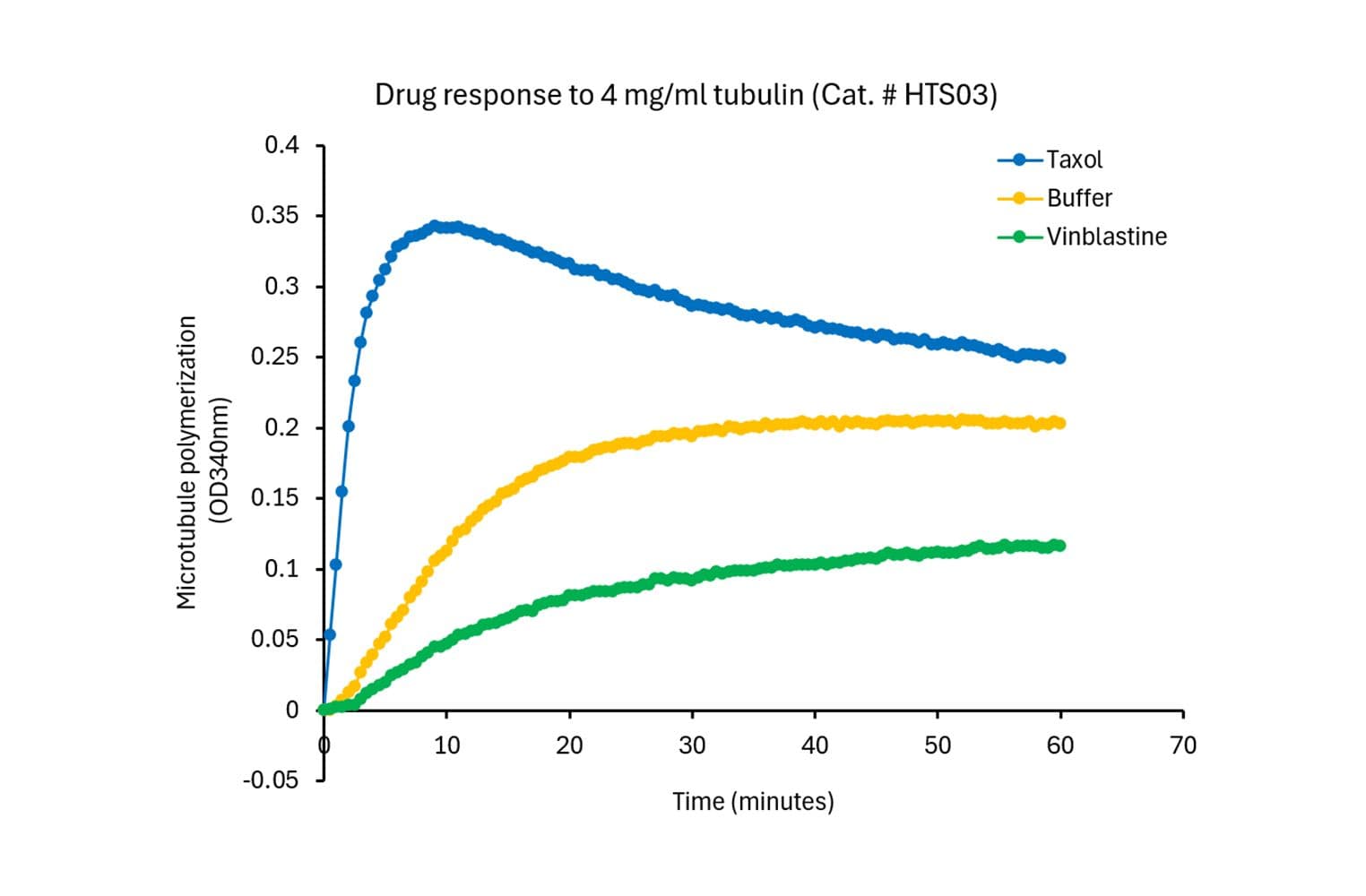
The biological activity of HTS03 is evaluated using a tubulin polymerization assay, which monitors microtubule formation by measuring absorbance at 340 nm. Under the test conditions (4 mg/ml tubulin in General Tubulin Buffer plus 1 mM GTP, 100 µl volume, 37 °C, 0.8 cm pathlength), the OD340nm should reach between 0.10 and 0.15 within 30 minutes.
Cat. #HTS03