Microtubule-binding proteins (MTBPs) regulate the dynamic behavior and stability of microtubules, essential for intracellular transport, cell shape, and division. By binding to tubulin or microtubule lattices, they control polymerization, depolymerization, and interactions with other cytoskeletal components.
A native microtubule-associated protein (MAP) fraction has been isolated from bovine brain by temperature-induced tubulin polymerization and ionic exchange chromatography.
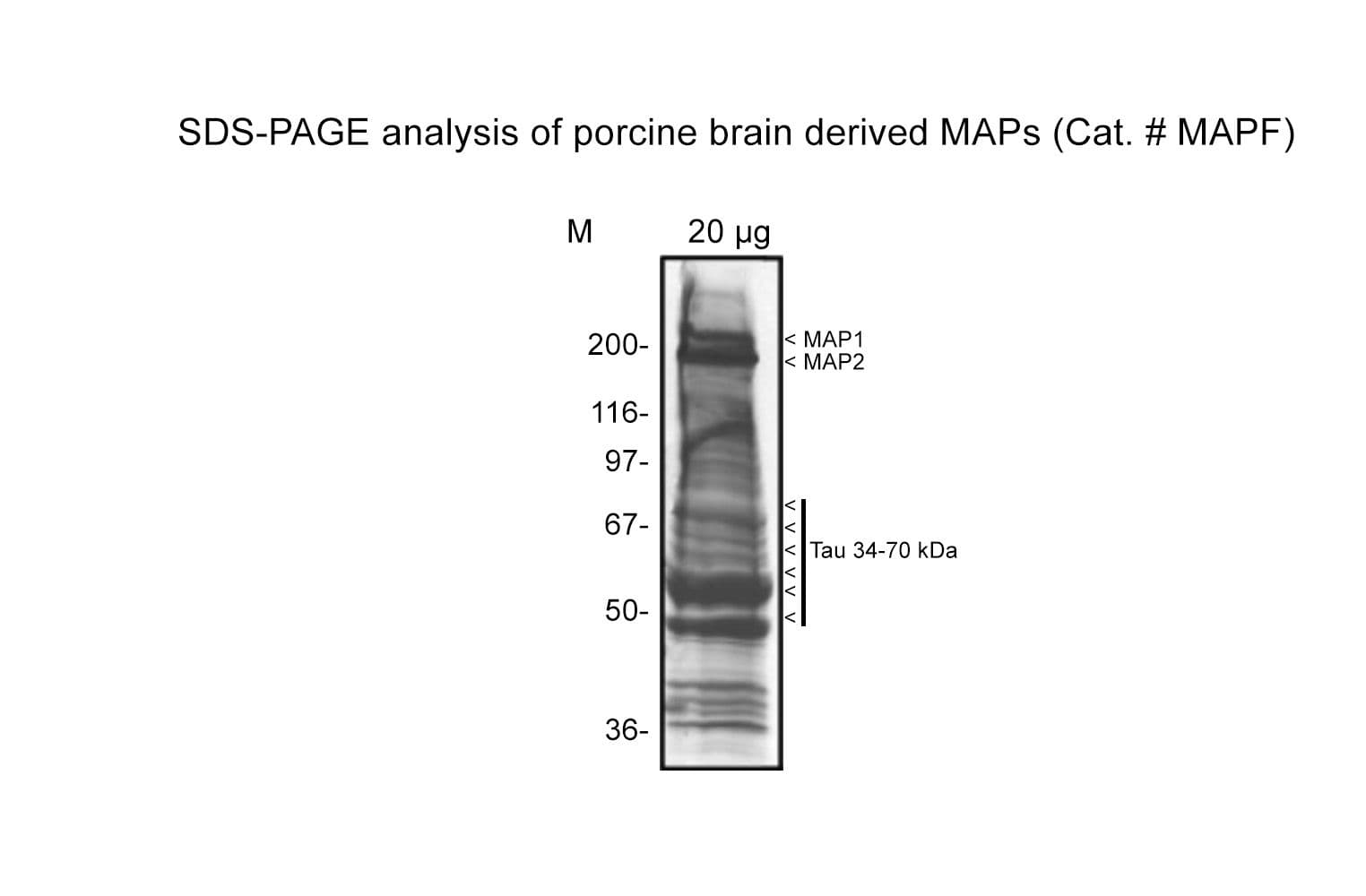
Protein purity is assessed by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on a12% polyacrylamide gel. Major MAPs present are MAP1 & 2 (~250 kDa) and Tau (37-70 kDa).
The biological activity of the MAP fraction can be determined by the ability of 0.1 mg/ml MAP fraction to enhance the polymerization rate (Vmax) of purified bovine brain tubulin in vitro. Under the specified conditions, the MAP fraction protein will stimulate tubulin polymerization approximately five fold when compared to tubulin polymerization without MAP fraction. See datasheet for details.
Cat. #MAPF