Inhibitors
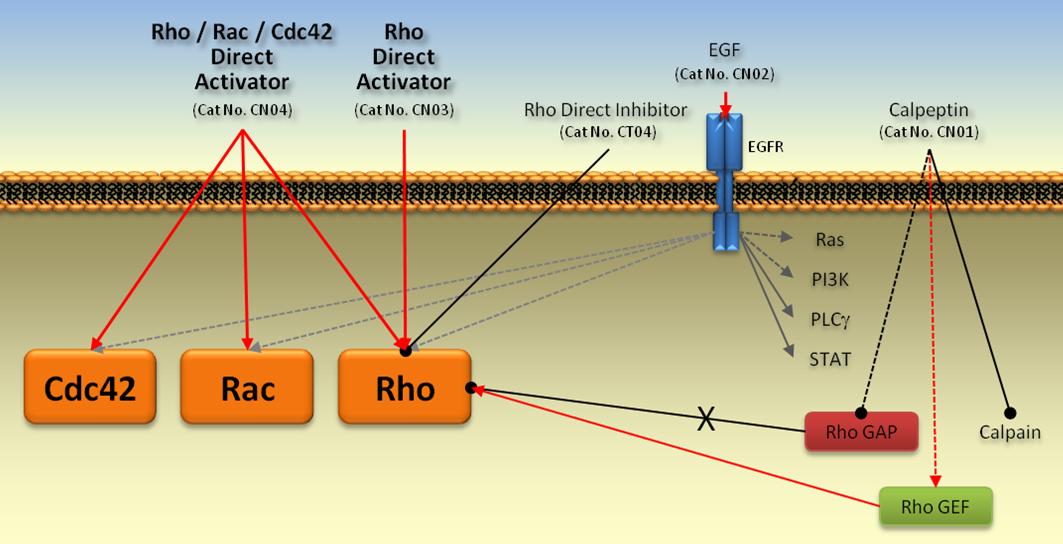
The G-switch line of Activators and Inhibitors are state of the art reagents for studying the effects of small G-proteins (SGPs) in your field of research. The Rho and Ras family of SGPs is important in cell motility, cell morphology, cell division, cell growth and proliferation, hence in many areas the activators and inhibitors can give you additional information about the mechanism and role of the pathway being investigated. The G-switch line has been developed to modify the endogenous SGP components rather than modifying their levels (as in siRNA studies) or introducing mutated forms which have other downstream effects (e.g., Rho Q63L). The results should at the least give a different perspective and ideally give you highly relevant information about the effects of modulating the endogenous SGP activity. For more information view our datasheets below.
Cytoskeleton's products have been cited hundreds of times over the past 18 years. A select few are described here, for more citations on individual products please use the "Citations" tab on each individual product page.
Rho Inhibitor I (Cat. # CT04)
Kim et al., 2009. Statins decrease dendritic arborization in rat sympathetic neurons by blocking RhoA activation. J. Neurochem. v 108, pp 1057-1071.
Martinelli et al., 2009. ICAM-1–mediated endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation via calcium and AMP-activated protein kinase is required for transendothelial lymphocyte migration. Mol. Biol. Cell. v 20, pp 995–1005.
Kakudo et al., 2011. The effect of C3 transferase on human adipose-derived stem cells. Hum. Cell. v 24, pp 4165-169.
Fan et al., 2011. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and CD74 Regulate Macrophage Chemotactic Responses via MAPK and Rho GTPase. J. Immunol. v 186 pp 4915-4924.
Ginestier et al., 2012. Mevalonate metabolism regulates basal breast cancer stem cells and is a potential therapeutic target. Stem Cells. v 30, pp 1327-1337.
Zhang et al., 2012. Self-Assembling Peptide Nanofiber Scaffold Enhanced with RhoA Inhibitor CT04 Improves Axonal Regrowth in the Transected Spinal Cord. J. Nanomaterials. doi:10.1155/2012/724857.
Kim et al., 2012. Inhibition of RhoA but not ROCK induces chondrogenesis of chick limb mesenchymal cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. v 418, pp 500-505.
Wan et al., 2012. Regulation of myosin activation during cell–cell contact formation by Par3-Lgl antagonism: entosis without matrix detachment. Mol. Biol. Cell. v 23, pp 2076-2091.
Balzer et al., 2012. Physical confinement alters tumor cell adhesion and migration phenotypes. FASEB J. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-211441.
Rho Pathway Inhinitor I (Cat. # CN06)
Bruśes J.L. 2013. Cell surface localization of a3b4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is regulated by N-cadherin homotypic binding and actomyosin contractility. PLoS ONE. 8: e62435.
Garrido-Gómez T., et al. 2012. Annexin A2 is critical for embryo adhesiveness to the human endometrium by RhoA activation through F-actin regulation. FASEB J. 26, 3715–3727.
Exoenzyme C3 transferase protein: His tagged: Clostridium botulinum recombinant (Cat. # CT03)
Benink, H. A. and Bement, W. M. (2005) J. Cell Biol. 168: 429-439.
Fleming, Y. M. et al. (2004) J. Cell Sci. 117: 2377-2388.
Mammoto, A. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279: 26323-26330.
Pellegrino, M. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279: 6526-6533.
Simpson, K. J. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64: 8694-8701.
Burakov, A. et al. (2003) J. Cell Biol. 162: 963-969.
Zhang, X. F. et al. (2003) Neuron 40: 931-944.
Valderrama, F. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 1560-1565.
Question 1: What is the selective range of CT04 in the Rho family of proteins.
Answer 1: C3 transferase, which forms the basis of CT04, is selective for RhoA, B, and C, but not Rac1 or Cdc42.
Question 2: What should I know about the "Rac inhibitor" NSC23766 ?
Answer 2: NSC23766 is not a classical inhibitor in the sense that it reduces the activity of all Rac1 activities or functions. In fact it has a limited range of target, it uncouples Rac from its GEF partners Tiam and Trio thus reducing the ability of these modulators to activate Rac. There are many other Rac GEFs in a cell so this inhibitor is quite restricted in its scope of targeting and should not be used as a general Rac inhibitor with out this knowledge.
- Exoenzyme C3 transferase protein: His tagged:Clostridium botulinum recombinant CT03Learn MoreExoenzyme C3 transferase protein: His tagged:Clostridium botulinum recombinant
- GDP dissociation inhibitor protein: GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant GDI01Learn MoreGDP dissociation inhibitor protein: GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant
- Rho GAP protein (catalytic domain): GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant GAS01Learn MoreRho GAP protein (catalytic domain): GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant
- Rho GAP protein:GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant GAP01Learn MoreRho GAP protein:GST tagged: Homo sapiens recombinant
-
-
