Cofilin 1 protein: human recombinant
Product Uses Include
- Studies of cofilin binding and severing activities
- Control protein for actin binding protein studies
Material
The human cofilin protein (isotype 1) has been produced in a bacterial expression system. The recombinant protein has a molecular weight of approximately 21 kDa, and does not contain a protein purification tag. Recombinant cofilin has been purified by ion exchange chromatography. Cofilin is one member of a large group of proteins characterized as “actin binding proteins” (ABPs). Cofilin is an essential cellular protein that can bind the barbed end of actin. In the cell, cofilin acts in concert with other regulatory proteins to mediate the response of the actin cytoskeleton to extracellular signals. In vertebrates, cofilin is regulated by pH, phosphorylation and phosphoinositides. Recombinant cofilin is supplied as a white lyophilized powder. The lyophilized protein is stable at 4°C desiccated (<10% humidity) for 1 year. When reconstituted with nanopure water, the protein will be in the following buffer: 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1 mM EGTA, 5% sucrose and 1% dextran. The reconstituted protein can be stored at -70°C for up to 6 months or at 4°C for up to 2 weeks with the addition of 100 µg/ml ampicillin and 5 µg/ml chloramphenicol witout any noticeable loss of activity.
Purity
Protein purity is determined by scanning densitometry of Coomassie Blue stained protein on a 4-20% gradient polyacrylamide gel. The Cofilin protein is 95% pure (see Figure 1).
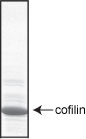
Figure 1. Cofilin protein purity determination. A 20 µg sample of CF01 (cofilin molecular weight approx. 21 kDa) was separated by electrophoresis in a 4-20% SDS-PAGE system, and stained with Coomassie Blue.
Biological Activity
The biological activity of recombinant cofilin is determined by its ability to bind and sever F-actin in a pH dependent manner. Below pH 7.0 cofilin binds to F-actin in a 1:1 molar ratio of cofilin to actin monomer in the filament. Above pH 7.0 cofilin will sever actin filaments and bind actin monomer in a 1:1 molar ratio. A standard biological assay for monitoring the actin binding and severing activity of cofilin consists of SDS-PAGE analysis of F-actin/cofilin spin down assays performed at pH 6.8 and 8.0. Stringent quality control ensures that at pH 6.8 only 20% of cofilin and actin are found in the supernatant, and that a 1:1 molar ratio of cofilin to actin protein is present in the pellet. Furthermore, at pH 8.0 approximately 80% of cofilin and actin are found in the supernatant due to the F-actin severing activity of cofilin.
For product Datasheets and MSDSs please click on the PDF links below. For additional information, click on the FAQs tab above or contact our Technical Support department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com
Question 1: After reconstituting the lyophilized protein with water, what is the composition of the buffer the cofilin protein is in?
Answer 1: The protein should be reconstituted to 5 mg/ml by the addition of 20 µl of distilled water. The protein will be in the following buffer; 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1 mM EGTA pH 8.0, 5% sucrose, and 1% dextran. In order to maintain high biological activity of the protein, it is strongly recommended that the protein solution be supplemented with DTT to 1 mM final concentration
Question 2: To separate the F-actin bound to cofilin, is it absolutely necessary to spin the sample at 100,000 x g?
Answer 2: If possible we recommend spinning the F-actin/cofilin complex at 100,000 x g to absolutely insure that the protein complex pellets. Check with your university’s core facilities or neighboring labs for access to an ultracentrifuge. However, in a pinch, spinning at 50,000 x g should pellet the majority of the complex.
If you have any questions concerning this product, please contact our Technical Service department at tservice@cytoskeleton.com